
plant growth and development notes for class 11 download in pdf, seeds online, rose seeds, strawberry seeds, aloe vera seeds, buy seeds online, potato seeds, orchid seeds, online seeds, bamboo seeds, lavender seeds, bonsai tree seeds, stevia seeds, tulip seeds, free seeds, gerbera daisy seeds, chrysanthemum seeds, seeds for sale, orchids seeds, fuchsia seeds, seeds and seeds… , plant growth and development 11 notes, class 11 biology notes, plant growth and development class 11, plant growth and development class 11 notes, class 11 plant growth and development, note biology, biology notes, plant growth and development, class 11 cbiology chapter 15 notes, 11th standard biology notes, 11th std biology notes, class 11 biology notes chapter 15, plant growth and development chapter
Abscission : Shedding of plant organs like leaves, flowers and fruits etc.
from the mature plant.
Apical dominance : Suppression of the growth of lateral buds in presence
of apical bud.
Dormancy : A period of suspended activity and growth usually associated
with low metabolic rate.
Photoperiodism : Response of plant to the relative length of day and night
period to induce flowering.
Phytochrome : A pigment, which control the light dependent developmental
process.
Phytohormone : Chemicals secreted by plants in minute quantities which
influence the physiological activities.
Senescene : The last phase of growth when metabolic activities decrease.
Vernalisation : A method of promoting flowering by exposing the young
plant to low temperature.
Growth : An irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ or its parts
or even of an individual.
Abbreviations
IAA Indole acetic acid
NAA Naphthalene acetic acid
ABA Abscissic acid
IBA Indole-3 butyric acid
2.4D 2.4 dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
PGR Plant growth regulator
Measurement of growth : Plant growth can be measured by a variety of
parameters like increase in fresh weight, dry weight, length, area, volume and
cell number.
Phases of growth : The period of growth is generally divided into three
phases, namely, meristamatic, elongation and maturation.
(i) Meristematic zone : New cell produced by metotic division at root-tip
and shoot tip thereby show increase in size. Cells are rich in protoplasm and
nuclei.
(ii) Elongation zone : Zone of elongation lies just behind the meristematic
zone and concerned with enlargement of cells.
(iii) Maturation zone : The portion lies proximal to the phase of elongation.
The cells of this zone attain their maximum size in terms of wall thickning
and
protoplasmic modification.
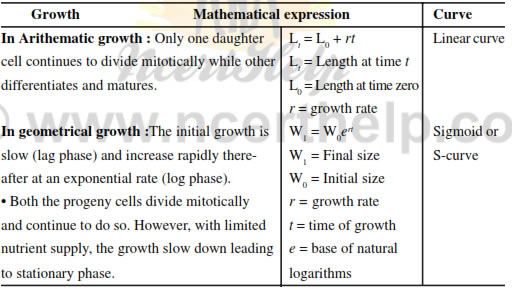
Growth rate : The increased growth per unit time is termed as growth rate.
The growth rate shows an increase that may be arithmetic or geometrical.
Differentiation : A biochemical or morphological change in meristemic
cell (at root apex and shoot apex) to differentiate into permanent cell is called
differentiation.
Dedifferentiation : The phenomenon of regeneration of permanent tissue
to become meristematic is called dedifferentiation.
Redifferentiation : Meristems/tissue are able to produces new cells that
once again lose the capacity to divide but mature to perform specific functions.
Growth promoting hormones : These are involved in growth promoting
activities such as cell division, cell enlargement, flowering, fruiting and seed
formation. e.g., Auxin, gibberellins, cytokinins.
Growth inhibitor : Involved in growth inhibiting activities such as dormancy
and abscission. e.g.,
Abscisic
acid and Ethylene.
 a
a
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.