
respiration in plants notes for class 11 download in pdf, respiration in plants, respiratory processes, the respiratory process, aerobic resp, aerobic respiratory, process of carbon dioxide, carbon processes, what is carbon gas , respiration in plants 11 notes, class 11 biology notes, respiration in plants class 11, respiration in plants class 11 notes, class 11 respiration in plants, note biology, biology notes, respiration in plants, class 11 cbiology chapter 14 notes, 11th standard biology notes, 11th std biology notes, class 11 biology notes chapter 14, respiration in plants chapter class 11 notes
Aerobic respiration : Complete oxidation of organic food in presence of
oxygen thereby producing CO
, water and energy.
Anaerobic respiration : Incomplete breakdown of organic food to liberate
2
energy in the absence of oxygen.
ATPSynthetase : An enzyme complex that catalyses synthesis of ATP during
oxidative phospho-relation.
Biological oxidation : Oxidation in a series of reaction inside a cell.
Cytochromes : A group of iron containing compounds of electron transport
system present in inner wall of mitochondria.
Dehydrogenase : Enzyme that catalyses removal of H atom from the
substrate.
Electron acceptor : Organic compound which recieve electrons produced
during oxidation-reduction reactions.
Electron transport : Movement of electron from substrate to oxygen through respiratory chain during respiration.
Fermentation : Breakdown of organic substance that takes place in certain
and
ethanol.
microbe like yeast under anaerobic condition with the production of CO.
Glycosis : Enzymatic breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid that occurs in
the cytoplasm.
Oxidative phosphorylation : Process of formation of ATP from ADP and
Pi using the energy from proton gradient.
Respiration : Biochemical oxidation food to release energy.
Respiratory Quotient : The ratio of the volume of CO
produced to the
volume of oxygen consumed.
Proton gradient : Difference in proton concentration across the tissue
membrane.
Mitochondrial matrix : The ground material of mitochondria in whichpyruvic acid undergoes aerobic oxidation through Kreb’s cycle.
Abbreviations
ATP − Adenosine tri phosphate
ADP − Adenosine di phosphate
NAD − Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide
NADP − Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide Phosphate
NADH − Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide
PGA − Phosphoglyceric acid
PGAL − Phospho glyceraldehyde
FAD − Flavin adenine dinucleotide
ETS − Electron transport system
ETC − Electron transport chain
TCA − Tricarboxylic acid
OAA − Oxalo acetic acid
FMN − Flavin mono nucleotide
PPP − Pentose phosphate pathway
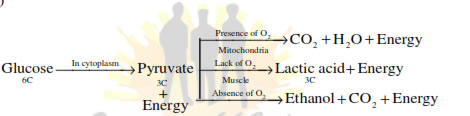
The overall mechanism of aerobic respiration can be studied under the
following steps :
(A) Glycolysis (EMP pathway)
(B) Oxidative Decarboxylation
(C) Kreb’s cycle (TCA-cycle)
(D) Oxidative phosphorylation
Glycolysis : The term has originated from the Greek word
glycos =
glucose
lysis = splitting or breakdown means breakdown of glucose molecule.
• It is also called Embeden-Meyerhof-Paranus pathway. (EMP pathway)
• It is common in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
• It takes place outside the mitochondria, in the cytoplasm.
• One molecule of glucose (Hexose sugar) ultimately produces two mol-
ecules of pyruvic acid through glycolysis.
• During this process 4 molecules of ATP are produced while 2 molecules
of ATP
are utilised.
Thus net gain of ATP
is of 2 molecules.
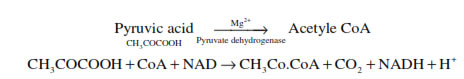
Oxidative decarboxylation : Pyruvic acid is converted into Acetyle CoA
in presence of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Tri Carboxylic Acid Cycle (Kreb’s cycle) or Citric acid Cycle : This
cycle starts with condensation of acetyle group with oxaloacitic acid and water
to yield citric acid which undergoes a series of reactions.
• It is aerobic and takes place in mitochondrial matrix.
• Each pyruvic acid molecule produces 4 NADH + H
+
, one FADH
, one
ATP.
• One glucose molecule has been broken down to release CO
and eight
molecules of NADH + H
+
, two molecules of FADH
and 2 molecules
of ATP.
2
Electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation : The metabolic
pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another,
is
called
Electron transport system and it is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
ETS comprises of the following :
(i) NAD and NADH + H
(ii) FAD and FADH
(iii) UQ
(iv) Cyt b, Cyt c
1
2
+
, Cyt c, Cyt a and Cyt a
.
Oxygen acts as final hydrogen acceptor. Oxidative phosphorylation takes
3
place in elementary particles present on the inner membrane of cristae of mitochondria.
Synthesis of ATP
from ADP and Pi using energy from proton gradient
is
called oxidative phosphorylation. In this process O
acceptor and it get reduced to water.
2
2
2
is the ultimate electron
Total ATP Production |
|
Process |
Total ATP produced |
| 1. Glycolysis | 2ATP + 2NADH (6ATP) = 8ATP |
| 2. Oxidative decarboxylation | 2NADH (6ATP) = 6ATP |
| 3. Kreb’s Cycle | 2GTP (2ATP) + 6NADH22 (18ATP) + 2FADH (4ATP) = 24ATP22 |
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.