
Define conductivity, Define molar conductivity, Discuss variation with concentration Chapter 3: Electrochemistry Chemistry Class 12 solutions are developed for assisting understudies with working on their score and increase knowledge of the subjects. Question 7:Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration. is solved by our expert teachers. You can get ncert solutions and notes for class 12 chapter 3 absolutely free. NCERT Solutions for class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3: Electrochemistry is very essencial for getting good marks in CBSE Board examinations
Question 7:Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration.
Answer:
Conductivity :–
Conductivity of a solution is equal to the conductance of a solution of 1 cm length and cross section area of 1 square cm. it may also be define as the conductance of ine centimeter cube of the conductor . It is represented by the symbol Kappa (κ). mathematically we can write
κ = 1/ p
here ρ is resistivity
the unit of K is ohm –1 cm –1 or S cm–1
The conductivity, κ, of an electrolytic solution depends on the concentration of the electrolyte, nature of solvent and temperature.
Molar conductivity:
Molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume V of solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with area of cross section A and distance of unit length. Therefore,
Distance is unit so l = 1
Volume = area of base × length
So V = A × 1 = A
Λm =κA/l
Λm = κV
Or
Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration. When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol Ë°m.
For strong electrolytes, Λ increases slowly with dilution and can be represented by the equation:
Λm = Ë°m° – A c ½
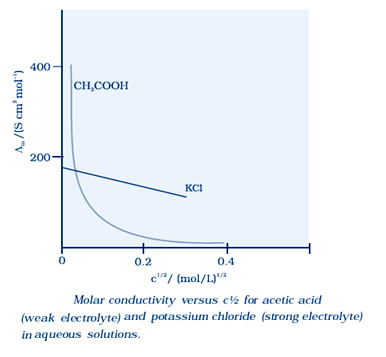
It can be seen that if we plot Λm against c1/2, we obtain a straight line with intercept equal to Ëm° and slope equal to ‘–A’. The value of the constant ‘A’ for a given solvent and temperature depends on the type of electrolyte i.e., the charges on the cation and anion produced on the dissociation of the electrolyte in solution.
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.