
polynomials class 9 maths notes with formulas download in pdf, polynomial 9 notes, class 9 maths notes, polynomial class 9, polynomial class 9 notes, class 9 polynomial, note maths, maths notes, polynomial, class 9 cmaths chapter 2 notes, 9th standard maths notes, 9th std maths notes, class 9 maths notes chapter 2, polynomial chapter class 9 notes
Constants : A symbol having a fixed numerical value is called a constant.
Example : 7, 3, -2, 3/7, etc. are all constants.
Variables : A symbol which may be assigned different numerical values is known avariable.
Example : ![]() cumference of circle
cumference of circle
r - radius of circle Where 2 & are constants. while C and r are variable
Algebraic expressions : A combination of constants and variables. Connected by some or all of the operations +, -, X and is known as algebraic expression.
![]()
Terms : The several parts of an algebraic expression separated by ’+’ or ’-’ operations are called the terms of the expression.
![]()
![]()
Polynomials : An algebraic expression in which the variables involved have only nonnegative integral powers is called a polynomial.
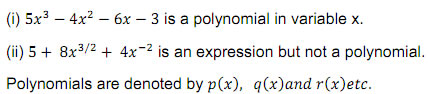
Coefficients : In the polynomial ![]() coefficient of
coefficient of ![]()
respectively and we also say that +1 is the constant term in it. Degree of a polynomial in one variable : In case of a polynomial in one variable the highest power of the variable is called the degree of the polynomial. Classification of polynomials on the basis of degree.

Classification of polynomials on the basis of no. of terms

Constant polynomial : A polynomial containing one term only, consisting a constanterm is called a constant polynomial the degree of non-zero constant polynomial is zero.
Zero polynomial : A polynomial consisting of one term, namely zero only is called a zero polynomial.The degree of zero polynomial is not defined.
Zeroes of a polynomial : Let p(x).be a polynomial. If ![]() then we say that is zero of the polynomial of p(x).
then we say that is zero of the polynomial of p(x).
Remark : Finding the zeroes of polynomial p(x) means solving the equation p(x)=0.
Remainder theorem : Let![]() be a polynomial of degree
be a polynomial of degree![]() and let a be any real number. When
and let a be any real number. When ![]() is divided
is divided![]() by then the remainder is
by then the remainder is![]()
Factor theorem : Let![]() be a polynomial of degree
be a polynomial of degree ![]() and let a be any real number.
and let a be any real number.
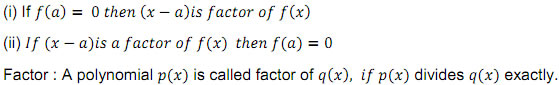
Factorization : To express a given polynomial as the product of polynomials each of degree less than that of the given polynomial such that no such a factor has a factor of lower degree, is called factorization.
![]()
Methods of Factorization : Factorization by taking out the common factore.g.
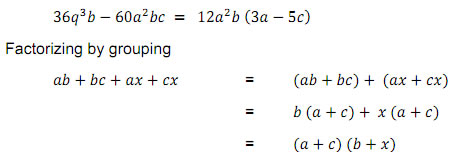
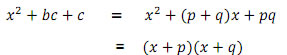
Identity : Identity is a equation (trigonometric, algebraic ) which is true for every value of variable.
Some algebraic identities useful in factorization:
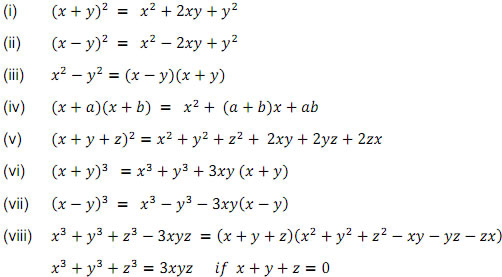
Q.1 Which of the following expressions is polynomial?
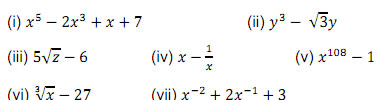
Q.2 Write the degree of each of the following polynomial.
![]()
Q.3 (i) Give an example of a binomial of degree 27.
(ii) Give an example of a monomial of degree 16.
(iii) Give an example of trinomial of degree 3.
Q.4 ![]()
Q.5 Find the zeros of the polynomials given below :
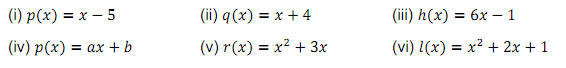
Q.6 Find the remainder when ![]() is divided by
is divided by![]()
Q.8 Find the value of a for which ![]() is a factor of the polynomial.
is a factor of the polynomial.
![]()
Q.9 Factorize the following expressions.
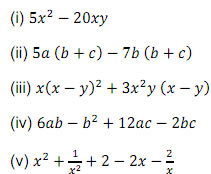
Q.10 Factorize :
![]()
![]()
Q.11 Factorize:
![]()
Q.12 Factorize following expressions.
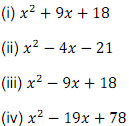
Q.13 Calculate
Q.13 Calculate (997)2 using algebraic identities.
Q.14 Calculate 103 X 107 using algebraic identities.
Q.15 Expand ![]()
Q.16 Factorize![]()
Q.17 Expand (i)![]()
Q.18 Evaluate (i) ![]()
Q.19 Factorize
![]()
Q.20 Factorize
![]()
Q.21 Factorize
![]()
Q.22 Find the product
![]()
![]()
Q.24 Which of the following expression is a polynomial?
![]()
Q.25 Degree of zero polynomial is
![]()
Q.26 For what value of k is the polynomial ![]() exactly divisible by
exactly divisible by![]()
![]()
Q.27 The zeroes of the polynomial p(x) ![]()
![]()
Q.28 ![]()
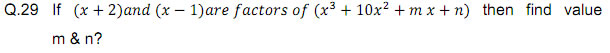
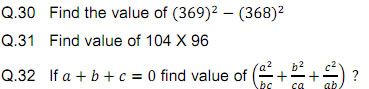
![]()
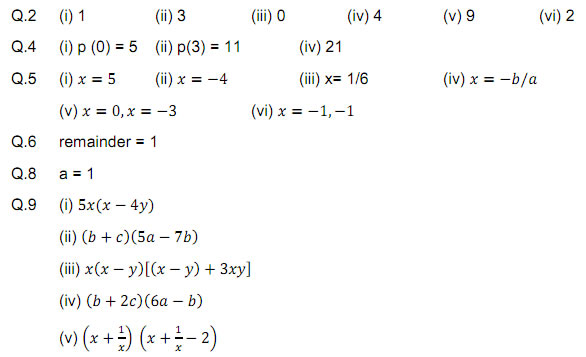
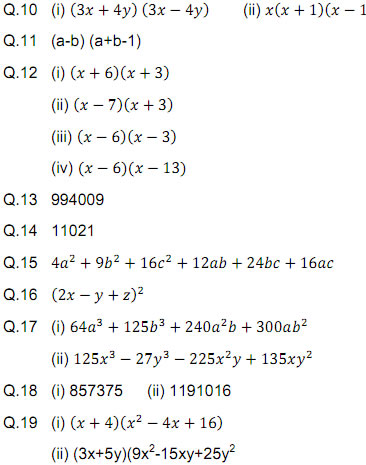


Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.