
ncert physics class 12 pdf, ncert physics class 12 pdf free download, ncert physics class 12 part 2 pdf, ncert physics class 12, physics ncert class 12 pdf, physics ncert class 12, ncert class 12 physics, ncert 12 physics, physics ncert class 11, physics class 12 ncert, class 12 physics ncert , electric charges and fields 12 notes, class 12 physics notes, electric charges and fields class 12, electric charges and fields class 12 notes, class 12 electric charges and fields, note physics, physics notes, electric charges and fields, class 12 cphysics chapter 1 notes, 12th standard physics notes, 12th std physics notes, class 12 physics notes chapter 1, electric charges and fields chapter class 12 notes
• Electrostatics is the study of charges at rest.
• The intrinsic property of fundamental particle of matter which give rise to
electric force between objects is called charge.
• Charging a body can be done by friction, induction and conduction.
• Properties of charges:
o Like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
o Charges are additive in nature ![]()
o Charges are quantized. i.e., Q= ± ne [n=1,2,3,… & e=1.602 X10-19 C]
o Charge on a body is independent of velocity of the body.
o Charge is conserved.
• The sensitive device which is used to identify whether the body is charged or not is called electroscope

• Dipole : Two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance.
• Dipole moment: Product of magnitude of either charge and distance of
separation between them. It is a vector. SI unit: Cm,![]() direction of
direction of ![]() is
from negative charge to positive charge along the straight line joining both the
charges.
is
from negative charge to positive charge along the straight line joining both the
charges.
• Dipole in a uniform electric field experiences no net translating force but
experiences a torque. ![]()
• ![]() • Electric field due to a short dipole
• Electric field due to a short dipole
✓Arbitrarily starts from +ve charge and end at –ve charge
✓ Continuous, without any breaks, never form closed loops
✓Never intersect
✓Relative closeness of the field lines represents the magnitude of the fieldstrength.
✓For a set of two like charges – lateral pressure in between
✓For a set of two unlike charges – longitudinal contraction in between.
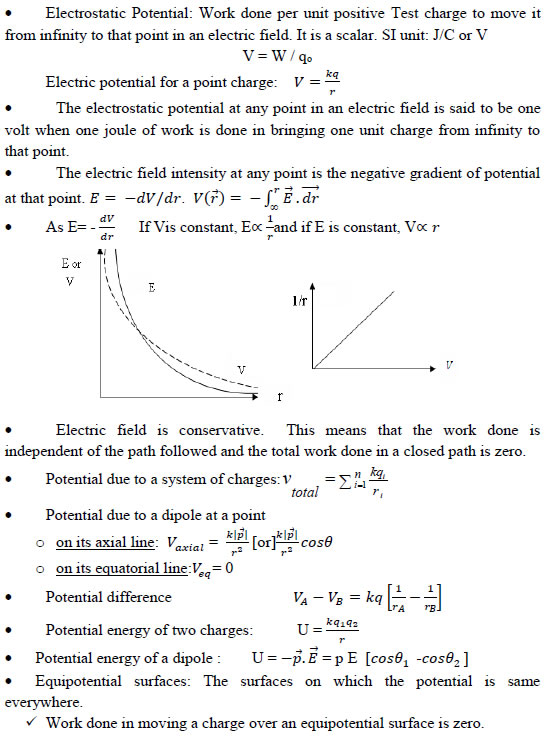
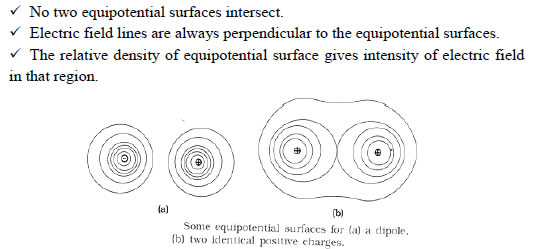
(i) Inside a conductor Electrostatic field is zero
(ii) On the surface E is always Normal to the surface
(iii) No excess charge resides inside the conductor
(iv) Charge distribution on the surface is uniform if the surface is smooth
(v) Electric field is zero in the cavity of hollow conductor and potential remains
constant which is equal to that on the surface.
• Capacitor: An arrangement of two conductors separated by a small distance
without any electrical contact between them is called capacitor.

• The dielectric is the substance which is essentially an insulator but behaves like a conductor in electrostatic situation.
• The dielectric having atom or molecules whose negative charge centre is not coinciding with positive charge centre is called polar dielectric. They have permanent dipole moments in the order of 10-30 Cm.
• The dielectric having atom or molecules whose negative charge centre is coinciding with positive charge centre is called non-polar dielectric.
• The dipole moment developed in non-polar dielectric due to external electric field is called induced dipole moment.
• The induced dipole moment per unit volume is called Polarisation Vector. The direction of polarisation vector is same as that of external electric filed.
• The ratio of electrostatic force in free space to that in medium OR the ratio of electrostatic field in free space to that in medium OR the ratio of absolute permittivity of medium to that of free space is called relative permittivity or dielecric constant of the medium.![]()
• The ratio of polarisation to ![]() times the electric field intensity is called electric susceptibility.
times the electric field intensity is called electric susceptibility. ![]() he dielectrics with constant
he dielectrics with constant ![]() are called linear dielectrics.
are called linear dielectrics.
• The maximum external electric field the dielectric can withstand without dielectric beakdown is called dielectric strength. SI unit Vm-1
• The capacitance of a spherical conductor of radius R is ![]()
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.