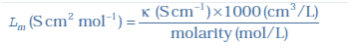Q-24 What is molar conductivity? Molar conductivity denoted by the symbol Λm (Greek, lambda). Molar conductivity of the solution is equal to conductivity at unity concentration
Mathematically
Molar conductivity,
Λm =c/κ
The unit of κ and concentration is S m
–1 and mol m
–3 respectively then the units of Λ
m are in S m
2 mol
–1.
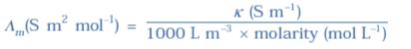
Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration.
What is limiting Molar conductivity ? When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as
limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol
Ëm°.
Exaplain the relation between molar conductivity and concentration? For strong electrolytes, Λ increases slowly with dilution and can be represented by the equation:
Λ
m =
Ëm° –
Ac ½ It can be seen that if we plot a Figure. Λm against c1/2, we obtain a straight line with intercept equal to Ëm° and slope equal to ‘–A’. The value of the constant ‘A’ for a given solvent and temperature depends on the type of electrolyte
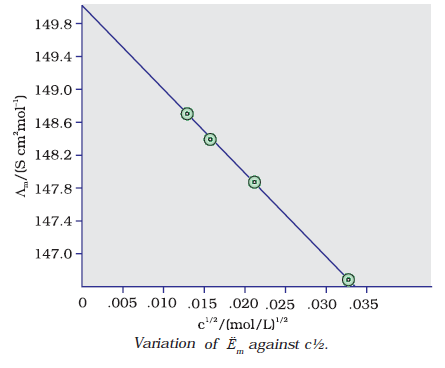
i.e., the charges on the cation and anion produced on the dissociation of the electrolyte in the solution. Thus, NaCl, CaCl2, MgSO4 are known as 1-1, 2-1 and 2- 2 electrolytes respectively. All electrolytes of a particular type have the same value for ‘
A’.