
Laws of Chemical Combination chapter 1 can study by students of class 11. These definitiona and formulas of Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry is developed and witten by our expert teachers. Chemistry formulas. Laws of Chemical Combination is prepapred and collected from varius resources to help the students.
LAWS OF CHEMICAL COMBINATIONS:
Law of Conservation of Mass
It states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed.
Law of Definite Proportions
It stated that a given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight.
Example : Oxygen and hydrogen in water always bear ratio of 16:2 or 8:1 by mass
Law of Multiple Proportions
According to this law, if two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Example
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
2g 16g 18g
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Hydrogen Peroxide
2g 32g 34g
Here, the masses of oxygen (i.e. 16 g and 32 g) which combine with a fixed mass of hydrogen (2g) bear a simple ratio, i.e. 16:32 or 1: 2.
Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes
when gases combine or are produced in a chemical reaction they do so in a simple ratio by volume
provided all gases are at same temperature and pressure.
Example
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
100 mL 50 mL 100 mL
Thus, the volumes of hydrogen and oxygen which combine together (i.e. 100 mL and 50 mL) bear a simple ratio of 2:1
Avogadro Law
Avogadro proposed that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain
equal number of molecules
Example .
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
we see that two volumes of hydrogen combine with one volume of oxygen to give two volumes of water without leaving any unreacted oxygen.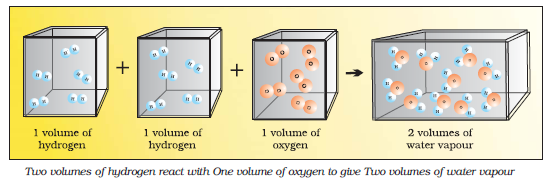
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.