DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY 1. Matter consists of indivisible atoms.
2. All the atoms of a given element have identical properties including identical mass. Atoms of different elements differ in mass.
3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio.
4. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of atoms. These are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
5.Dalton’s theory could explain the laws of chemical combination.
amu: One atomic mass unit is defined as a mass exactly equal to one twelfth the mass of one carbon - 12 atom.
1 amu = 1.66056×10
–24 g
Average Atomic Mass Many naturally occurring elements exist as more than one isotope. When we take into account the existence of these isotopes and their relative abundance (per cent occurrence),
Example
Carbon has three isotopes
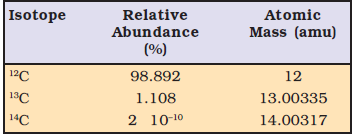
Average mass
= (0.98892) (12 u) + ( 0.01108) (13.00335 u) + (2 × 10
–12) (14.00317 u)
= 12.011 u
Molecular mass is the sum of atomic masses of the elements present in a molecule. It is obtained by multiplying the atomic mass of each element by the number of its atoms and adding them together.
Example
Molecular mass of methane,(CH4) = (12.011 u) + 4 (1.008 u) = 16.043 u
Formula mass The formula such as NaCl is used to calculate the
formula mass instead of molecular mass as in the solid state sodium chloride does not exist as a single entity.
Thus, formula mass of sodium chloride = atomic mass of sodium + atomic mass of chlorine
= 23.0 u + 35.5 u = 58.5 u

