
biology notes, biology notes for class 11, class 10 biology notes, biology notes for class 10 ,cbse class 10 science notes, cbse science, cbse 10 science notes, cbse 10 science, cbse 10th science notes , control and co-ordination 10 notes, class 10 science notes, control and co-ordination class 10, control and co-ordination class 10 notes, class 10 control and co-ordination, note science, science notes, control and co-ordination, class 10 cscience chapter 7 notes, 10th standard science notes, 10th std science notes, class 10 science notes chapter 7, control and co-ordination chapter class 10 notes
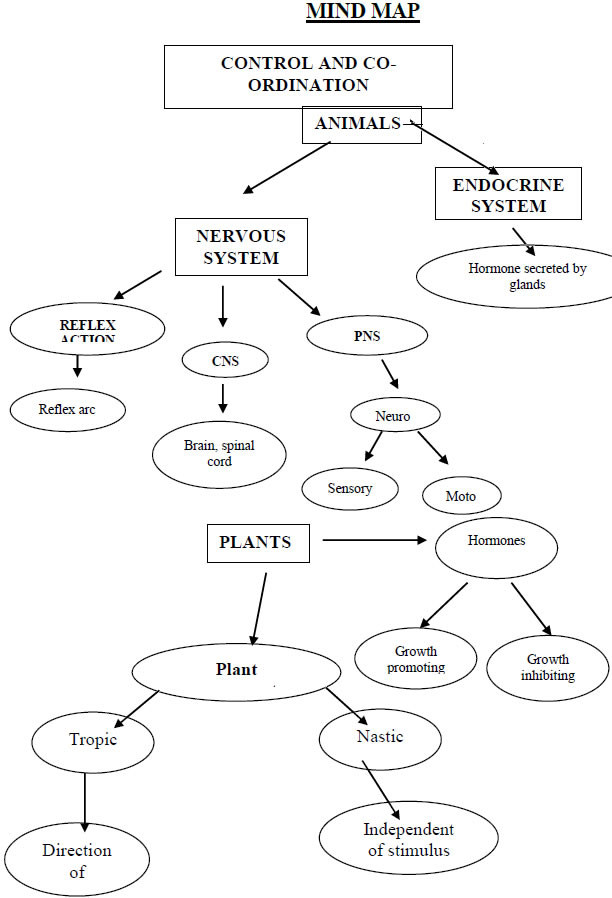
➣ Coordination-The working together of various organs of the body of an organism in a proper manner to produce appropriate reaction to a stimulus is called coordination.
➣ Stimulus- The changes in the environment to which an organism responds and reacts is called Stimulus
➣ Control & coordination in animals- takes place by (i) Nervous system & (ii) Endocrine system
➣ Nervous system
Stimulus → Receptor organ → Sensory nerve → Brain/Spinal cord
↓ Response ← Effector organ ← Motor nerve
➣ Endocrine system
Stimulus → Endocrine organ → Secrete hormone → Hormone in blood
↓
Response ← Target organ
➣ Parts of the Nervous system –
(i) Brain (ii) Spinal cord (iii) Nerves (Neurons)
➣ A Neuron is the structural & functional unit of Nervous system
➣ Parts of a neuron-
(i) Dendrites (ii) Cell body (iii) Axon
➣ Synapse- Space/junction between two adjacent nerves is called Synapse.
➣ Passing of information takes place –
(i) By Electric impulse (inside the neuron) and
(ii) In the form of chemicals (At synapse)
➣ Reflex action- Spontaneous, involuntary and automatic response to a stimulus to protect us from harmful situations. Eg. On touching a hot object unknowingly we instantly withdraw our hand.
➣ Reflex arc- The pathway of the reflex action is called Reflex arc.
Stimulus → Receptor organ → Sensory nerve → Spinal cord →Effector organ→ Response
Refer to figure 7.2 page no. 117 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
➣ Nervous system-
(1) Central Nervous system (CNS)
(2) Peripheral Nervous system(PNS)
(i) Brain (i) Autonomic Nervous system
(ii) Spinal cord (ii) Voluntary Nervous system
➣ Brain
(i) Centre of coordination of all activities
(ii) Thinking is involved
(iii) Complex process
➣ Parts of brain-
Refer to figure 7.3 page no. 118 of N.C.E.R.T Text book
Fore brain |
Mid brain |
Hind brain |
(i) Cerebrum |
---------- |
(i) Cerebellum |
➣ Fore brain
Cerebrum-
(i) Main thinking and largest part of the brain.
(ii) It has 3 main areas-
a) Sensory area- to receive impulses from sense organs via Receptors
b
) Motor area- control voluntary movements.
c) Association areas- Reasoning, learning & intelligence. Thalamus – It relays sensory information to the Cerebrum
Hypothallamus- It forms the link between Nervous system & Endocrine system
➣ Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears
➣ Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brain
Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium.
Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord
Medulla oblongata- Controls involuntary actions like blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
➣ Spinal cord- Cylindrical or tubular structure extending downwards from the Medulla oblongata.
➣ Protection of the brain & the spinal cord-
(i) Bony outer covering: skull for the brain & vertebral column for the spinal cord.
(ii) Cerebrospinal fluid present in between the three membranes.
➣ Action caused by Nervous tissue
Information → Nervous tissue → Brain Muscles → Causes action
➣ Path or action-
Nerve impulse → Muscle cell → Changes shape due to special proteins
↓
Action caused ← Shorter form of muscles ← Change shape & arrangement of cell
➣ Chemical communication by hormones- (advantages)
(i) Electrical impulses have their limitations because they reach only those cells connected to the nervous tissue.
(ii) Also the nerve cells cannot generate & transmit impulses continuously.
iii)Electrical communication is slower.
➣
Hormones-
(i) are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands
(ii) Are secreted in small amounts & may act in nearby places or distant places.
(iii) Do not take part in the reaction & are destroyed immediately.
➣ Hormones are secreted by- Endocrine glands & Exocrine glands
S. No. |
Endocrine glands |
Exocrine glands |
1. |
Ducts absent |
Ducts present |
2. |
Secrete hormones |
Secrete enzymes |
3. |
Secreted in blood |
Secreted in ducts of glands |
4. |
Situated away from the site of action |
Situated near the site of action |
➣ Some glands which act as both endocrine & exocrine
Gland |
Endocrine function |
Exocrine function |
Pancreas |
Produces insulin & Glucagon |
Produces digestive enzyme. (pancreatic |
Testes |
Produces hormone |
Produces male gametes (reproductive cells) |
Ovaries |
Produces hormone Oestrogen |
Produces female gametes (reproductive |
➣ Important Endocrine glands, the hormone they secrete & their function
Refer to figure 7.7 page no. 124 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
Endocrine gland |
Hormone |
Function |
Pituitary gland |
Growth hormone |
Body growth, development of bones & muscles |
Thyroid gland |
Thyroxine |
Regulates carbohydrate, protein & fat |
Pancreas |
Produces insulin & |
Regulates blood sugar levels (if less diabetes is |
Testes in males |
Produces hormone |
Development of secondary male characters like |
Ovaries in |
Produces hormone |
Development of secondary female characters like |
➣ Coordination in plants- Only chemical coordination is present in plants.
➣ Tropic movements- The movements of plants in the direction of stimulus (positive) or away from it (negative) are called tropic movements. E.g. Phototropism, Geotropism. Chemotropism.
Refer to figure 7.4 & 7.5 page no. 121 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
➣ Nastic movements -The movements of plants independent of stimuli are called nastic movements. E.g.- Touch me not plant leaves close when touched.
➣ Plant hormones (Phytohormones) Examples-
1. Auxins- Help in growth of root & shoot tips.
2. Gibberellins- Help in vegetative growth
3. Cytokinins- Promote cell division
4. Abscissic acid - Inhibits growth & causes wilting (falling) of leaves
➣ Important diagrams-
1. Structure of neuron (nerve cell)
2.Reflex arc
3.Human brain
4.Endocrine glands .
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.