
class 9 science notes, chapter 1 matter in our surroundings, notes of matter in our surroundings, class 9 science, matter in our surroundings 9 notes, class 9 science notes, matter in our surroundings class 9, matter in our surroundings class 9 notes, class 9 matter in our surroundings, note science, science notes, matter in our surroundings, class 9 cscience chapter 1 notes, 9th standard science notes, 9th std science notes, class 9 science notes chapter 1, matter in our surroundings chapter class 9 notes
Anything that occupies space and has mass and is felt by senses is called matter. Matter is the form of five basic elements the Panch tatva – air , earth ,fire , sky and water.
•Made of tiny particles.
•Vacant spaces exist in particles.
•Particles are in continuous motion.
•Particles are held together by forces of attraction.
• Based upon particle arrangement
• Based upon energy of particles
• Based upon distance between particles
SOLID |
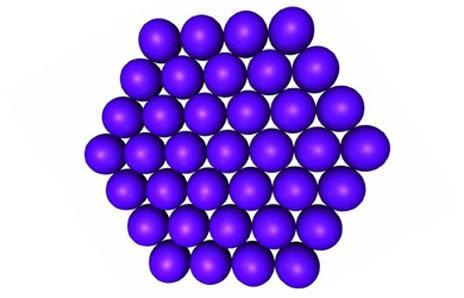 |
| Fixed shape and definite volume . |
| Inter particle distances are smallest. |
| Incompressible. |
| High density and do
not diffuse. |
| Inter particle forces of attraction are strongest. |
| Constituent particles are very closely packed. |
LIQUID |
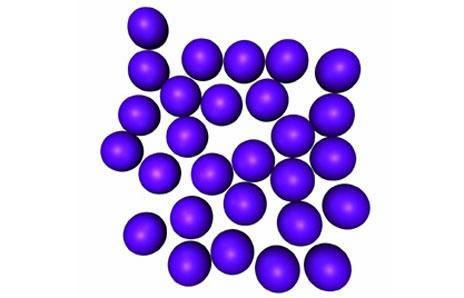 |
| Not fixed shape but fixed volume. |
| Inter particle distances are larger. |
| Almost incompressible. |
| Density is lower than
solids and diffuse. |
| Inter particle forces of attraction are weaker than solids . |
| Constituent particles are less closely packed. |
GAS |
 |
| Neither fixed shape nor fixed volume. |
| Inter particle distances are largest. |
| Highly compressible. |
| Density is least and
diffuse. |
| Inter particle forces ofattraction are weakest |
| Constituent particles are free to move about. |
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings (www.ncerthelp.com)
• A plasma is an ionized gas.
• A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by
magnetic fields.
• Plasma, like gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite
volume. Ex. Ionized gas
• A BEC is a state of matter that can arise at very low
temperatures.
• The scientists who worked with the Bose-Einstein
condensate received a Nobel Prize for their work in 1995.
• The BEC is all about molecules that are really close to eachother (even closer than atoms in a solid).
1. Solids have a definite shape and a
definite volume because the
particles are locked into place.
2. Solids do not flow easily because
the particles cannot move/slide
past one another.
3. Solids are not easily compressiblebecause there is little free space
between particles .
1. Liquids are not easily compressible
and have a definite volume because
there is little free space between
particles.
2. Liquids have an indefinite shape
because the particles can lide
past one another.
3. Liquids flow easily because the particles can move/slide past
one another.
1. Gases are easily compressible
because there is a great deal of
free space between particles
2. Gases flow very easily because
the particles randomly move past
one another.
3. Gases have an indefinite shape
and an indefinite volume becausethe particles can move past oneanother.
1. Plasmas have an indefinite shape
and an indefinite volume because
the particles can move past one
another.
2. Plasmas are easily compressible
because there is a great deal of
free space between particles.
3. Plasmas are good conductors of
electricity &are affected by
magnetic fields because they are
composed of ions
1. Particles are less energetic than
solids because Exist at very low
temperature .
2. Particles are literally
indistinguishable because they
are locked into same space
3. BEC shows superfluidity because
Particles can flow without
friction.
Matter Can Change its State
Water can exist in three states of matter –
• Solid, as ice ,
• Liquid, as the familiar water, and
• Gas, as water vapour.
The changing of solid directly into vapours on heating & vapours into solid on
cooling. Ex. Ammonium chloride , camphor & iodine.
a) Effect of change in temperature
The temperature effect on heating a solid varies depending on the nature of the solid
& the conditions required in bringing the change .
• On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases
which overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles thereby solid melts
and is converted to a liquid.
• The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric
pressure is called its melting point.
• The melting point of ice is 273.16 K.
• The process of melting, that is, change of solid state into liquid state is also known as
fusion.
b) Effect of Change of Pressure
• Increasing or decreasing the pressure can change the state of matter. Applying
pressure and reducing temperature can liquefy gases.
• Solid carbon dioxide (CO2 ) is stored under high pressure. Solid CO2
gets converted
directly to gaseous state on decrease of pressure to 1 atmosphere without coming
into liquid state. This is the reason that solid carbon dioxide is also known as dry ice.
The hidden heat which breaks the force of attraction between the molecules during change of state.
Fusion |
Vaporisation |
| Heat energy required to change 1kg of solid into liquid. | Heat energy required to change 1kg of liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure atits boiling point. |
• Particles of matter are always moving and are never at rest.
• At a given temperature in any gas, liquid or solid, there are particles with different
amounts of kinetic energy.
• In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher
kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other
particles and gets converted into vapour .
• This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature below its
boiling point is called evaporation.
• The rate of evaporation increases with an increase of surface area.
• With the increase of temperature, more number of particles get enough kinetic energy
to go into the vapour state.
• Humidity is the amount of water vapour present in air. The air around us cannot hold
more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature. If the amount
of water in air is already high, the rate of evaporation decreases.
• Wind speed : the higher the wind speed , the more evaporation.
The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surrounding to regain the energy lost
during evaporation,
• Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk (whole) of the liquid change
into vapour state.
• Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. Particles from the surface gain enough
energy to overcome the forces of attraction present in the liquid and change into the
vapour state.
• Kelvin is the SI unit of temperature, 00
C =273.16 K. we take 00C = 273 K.
• SI unit of temperature is Kelvin. T (K)= T ( o0C) +273
• Kelvin scale of temperature has always positive sign , hence regarded as better scale
than Celsius.
• Atmosphere (atm) is a unit of measuring pressure exerted by a gas. The SI unit of
pressure is Pascal (Pa):
• 1 atmosphere = 1.01 × (10 to the power 5) Pa. The pressure of air in atmosphere is called
atmospheric pressure. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atmosphere, and is
taken as the normal atmospheric pressure.
Q.1 Define matter.
Q.2 What happens if you put copper sulphate crystals in water?
Q.3 A substance has a definite volume but no definite shape ? State whether this
substance is a solid , a liquid or a gas.
Q.4 Arrange the following substances in increasing order of force of attraction between the
particles. (a) Milk (b) Salt (c) Oxygen.
Q.5 A substance has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume . State whether it is a solid ,
a liquid or a gas.
Q.6 The melting point of a substance is below the room temperature . Predict its physical
state.
Q.7 What is vapour ?
Q.8 Name the temperature at which the solid and liquid states of substance can exis together .
Q.9 What is the effect of pressure on boiling point?
Q.10 Name any two substances which sublime.
Q.11 Define Condensation.
Q.12 For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the
change of state?
Q.13 Which is the slow process , Evaporation or Boiling ?
Q.14 State the effect of surface area on rate of evaporation.
Q.15 Why are we able to sip hot tea faster from saucer rather than from a cup?
Q.16 What is the SI unit of temperature?
Q.17 why kelvin scale of temperature is regarded as better scale than Celsius?
1. Pressure on the surface of a gas is increased. What will happen to the inter particle
forces?
2. Name the three states of matter.
3. What happens when a liquid is heated ?
4. A gas can exert pressure on the walls of the container. Assign reason.
5. Convert the following temperature to Kelvin Scale (a) 100°C (b) 37°C
6. What is meant by density?
7. Give the characteristics of the particles of matter.
8. Water droplets seen on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water is due
to _____________ .
9. Change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through liquid sate is
called _____________________ .
10. __________________ is a surface phenomenon.
1. Define Latent heat of vaporisation.
2. Explain why temperature remain constant during the change of state of any
substance?
3. Define Sublimation with examples.
4. *Do we sweat more on a dry day or humid day ? Justify your reason.
5. Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice cold
water?
6. Convert the following temperature to the Kelvin scale (a) 25°C (b) 373°C
7. List two properties that liquids have in common with solids.
8. List two properties that liquids have in common with gases.
9. *What will happen to the melting point temperature of ice if some common salt is
added to it? Justify your answer.
10. *How will you show that air has maximum compressibility?
1. Define the term (a) Latent heat of fusion (b) Latent heat of vaporization
2. *State the effect of (i) surface area (ii) nature of the liquid on the rate of evaporation.
3. *Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have
observed that ice floats on water. Why?
4. What is the physical state of water at 250°C, 100°C, 0°C?
5. Give reasons :
i) A sponge can be pressed easily; still it is called a solid.
ii) Water vapours have more energy than water at same temperature.
6 . What are intermolecular forces ? How are these related to the three states of matter ?
7. Is it possible to liquify atmospheric gases? If yes, suggest a method.
1. a) What is meant by evaporation? What are the factors on which the rate of
evaporation depend upon?
b) How does evaporation causes cooling?
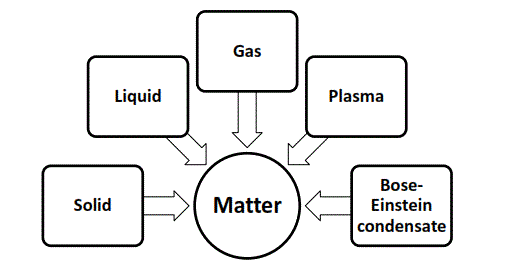
2. State the properties of all the five states of matter.
3. Define : Melting point , Freezing point & Boiling point
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.