
plant kingdom classification, classification of plant kingdom, classification of plants kingdom, plant kingdom classification chart, classification of plant kingdom with diagram, biology classification of plant kingdom, kingdom classification, classification of kingdom plantae, plants kingdom classification, plant kingdom classification for kids, plant and animal kingdom classification, classification of the plant kingdom , plant kingdom 11 notes, class 11 biology notes, plant kingdom class 11, plant kingdom class 11 notes, class 11 plant kingdom, note biology, biology notes, plant kingdom, class 11 cbiology chapter 3 notes, 11th standard biology notes, 11th std biology notes, class 11 biology notes chapter 3, plant kingdom chapter class 11 notes
| 1- | Phylogeny | - | Evolutionary history of organism . | |
| 2- | Zoospores | - | Motile spores with flagella . | |
| 3- | Gametophyte | - | Haploid stage of plant, producing gametes. | |
| 4- | Sporophyte | - | Diploid stage of plants producing spores. | |
| 5- | Archegonium | - | Female reproductive structure. | |
| 6- | Antheridium | - | Male reproductive structure. | |
| 7- | Megasporangium | - | The structure which bears megaspores. | |
| 8- | Sporophyll | - | Leaf bearing sporangia producing spores. |
| - | Numerical taxonomy | - | based on several features compared collectively by computer. | ||
| - | Cytotaxonomy | - | based on cytological features. | ||
| - | Chemotaxonomy | - | based on chemical constituent. | ||
| Algae – | |||||
| - | Group of chlorophyllous, simple, thalloid plants. | ||||
| - | Largely aquatic, grow on soil, stone, wood etc or symbiotic. | ||||
| - | Unicellular to large filamentous. | ||||
Economically useful as-
a) Large photo synthesiser, release 02 .
b)Food for aquatic animals, humans.
c)Produce Algin (Brown algae), carrageen (red algae), agar (gelidium, gracilaria)
| Chlorophyceae | Phaeophyceae | Rhodophyceae |
- Green algae chlorophyll a&b dominant. |
-Brown algae. |
- phycoerythrin (dominant) and others chlorophyll a and d. |
Group of autotrophic plants with thallus having true roots, stem and leaves with multi cellular sex organs.
Occurs on damp, humid and shaded soil.
Root like rhizoids present.
-Main plant body gametophyte bears Antheridia and Archegonia. Biflagellate antherozoids produced from Antheridium and reach through water to egg in Archegonium.
-Zygote forms sporophyte which produces haploid spores to give rise to new plants.
Types of Bryophytes
Liverworts |
Mosses |
1.Thallus dorsiventrally flattened (Liver shaped), leafy members with leaf like appendages.
Marchantia |
- Thallus : Two stages (gametophyte) – Vegetative by Fragmentation of protonema &capsule.
Funaria |
| Pteridophyte: | |||
| - | Group of first terrestrial plants having vascular tissue viz. Xylem & Phloem. | ||
| - | True stem, root & leaf. | ||
| - | Found on damp, shady places. Sporophyte makes main plant body. | ||
| - | Sporophylls of Sporophyte bear sporangia (sori) onventral side producing haploid spores. | ||
| - | spores give rise to Prothallus which is leafy & autotrophic. | ||
| - | Prothallus bears sex organs – male – Antheridium and female- Archegonium. | ||
| - | Fertilisation leads into zygote formation which produces diploid Sporophyte. | ||
| Heterospory and Seed habit: | |||
| - | Two types of spores Microspore and Megaspore are produced in some members viz. Selaginella, Salvinia. | ||
| - | called Heterospory. | ||
| - | Heterospory is considered as begining of seed habit in terrestrial plants. | ||
| eg. Pteris, Dryopteris etc. | |||
| GYMNOSPERMS | |||
| - | Medium sized trees and shrubs. | ||
| - | Main plant body Sporophyte | ||
| - | In some members roots may have fungal association called Mycorrhiza. | ||
| -bilus. | |||
| - | Microspore i.e. pollens reaches to ovules.Pollen tubes help to transfer male gametes up to egg of archegonia present in female gametophyte of ovule.
|
||
| Zygote develops in an embryo inside seed | |||
| - | e.g. Cycas, Pinus ,Cedrusetc. | ||
| ANGIOSPERMS | |||
| Large no. of plants in varied habitats, small microscopic plants (Wolfia) to large trees | |||
| - | Group of plants having covered seeds in fruits. | ||
| - | Produce flowers having reproductive organs. | ||
| - | Most evolved plants. |
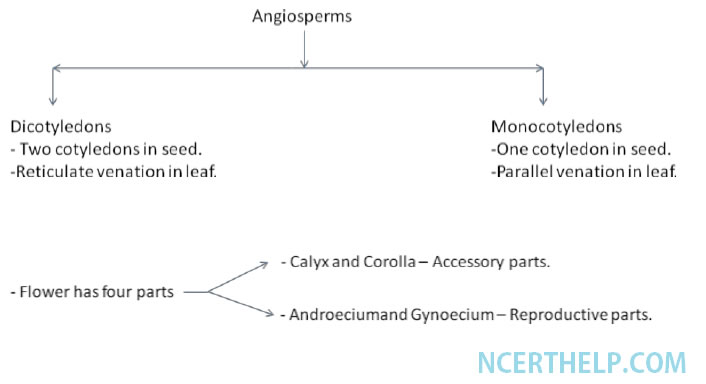
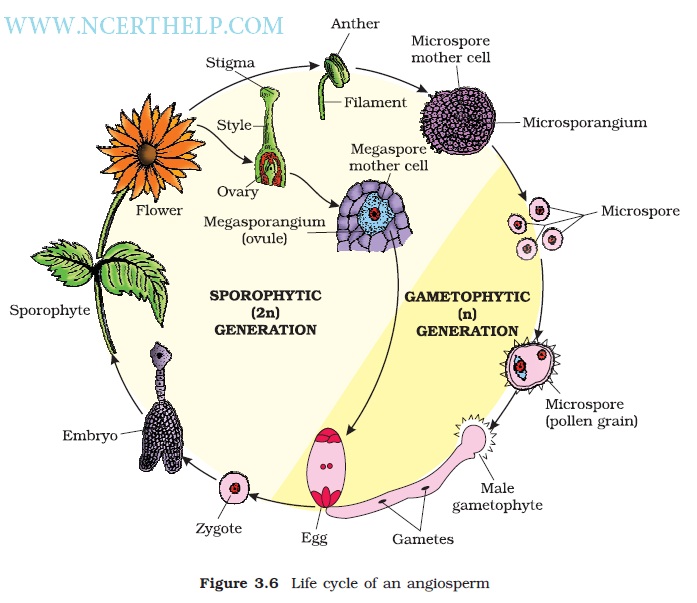
-Androecium is male part and one unit is stamen.
-Gynoecium is female part and one unit is carpel and has ovules.
-Ovule bears embryo sac.
-Embryo sac is seven celled and has Egg
01 – haploid. Synergids
02 – haploid.
Antipodals
03 - haploid. Secondary nucleus
04 – diploid.
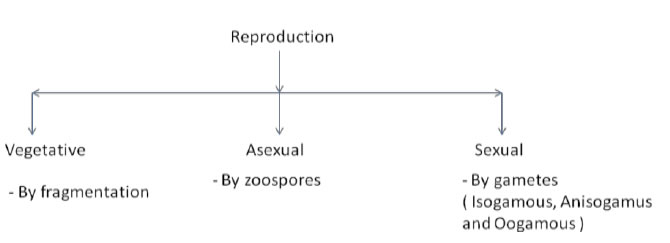
-Reproduction by vegetative and sexual methods.
-In sexual reproduction pollens shed off and reach to stigma of Gynoecium by pollination.
-Pollen germinates to form pollen tube with two male gametes and one tube nucleus.
-One gamete fuses with egg (Syngamy) and other with secondary nucleus to form PEN (primary endosperm nucleus). The whole process is called Double fertilization.
-Zygote forms embryo and PEN forms Endosperm in ovule which changes into seed inside fruit.
-Ovary wall changes into Pericarp (fruit wall).
-Alternation of generation occours.
Plant life cycle and alternation of Generation –
-Alternate stages of haploid (n) and Diploid (2n) phase in life cycle of plants.
Haplontic |
Diplontic |
Haplodiplontic |
- Dominating phase haploid
(n). eg. Algae viz. Ulothrix,Spirogyra etc. |
-Dominating phase diploid |
-Intermediate i.e.haploid & eg. Bryophytes & Pteridophyte. |
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.