
ncert solutions, free ncert solutions, solutions of ncert, ncert solutions online, ncert solutions for, ncert solutions free, online ncert solutions, solutions ncert, ncert solutions for class 1 , the living world 11 notes, class 11 biology notes, the living world class 11, the living world class 11 notes, class 11 the living world, note biology, biology notes, the living world, class 11 cbiology chapter 1 notes, 11th standard biology notes, 11th std biology notes, class 11 biology notes chapter 1, the living world chapter class 11 notes
1. Diversity : Large variety of anything.
2. Biodiversity : Large variety of organisms.
3. Nomenclature: Scientific naming of organisms.
4.
Identification : Correct description of organism prior to nomenclature.
5. Classification : Grouping of organisms in to categories on the basis of similarities & differences.
6. Taxon : Concrete biological object or category of classification.
1. Taxonomy : Process of classification of organisms.
2.
Systematics : branch of biology dealing with taxonomy along with evolutionary relationship between organisms.
3. Species : Group of Individual organisms with fundamental
similarities (with capacity if sexually reproducing).
1. Concentrate on minute points of the chapter keeping very short answer& short answer type questions in mind.
2. Emphasise on concepts.
-Objects having characteristics of cellular organisation,growth,reproduction,ability to sense environment & give response, metabolism etc.
-Increase in mass or number of cells characterise growth.
-plants grow throughout life.
-Animals grow to certain age .
-Non living objects also grow externally by accumulation of material on surface.
-Living objects grow from inside.
-Growth cannot be considered as defining property of living beings.
NB : There are certain examples in which mass is decreased during growth eg. Germinating potato tuber.
-Characteristics of living beings to produce progenies possessing features of their own type.
-Reproduction is of sexual& asexual type.
-Fungi produce spores for asexual reproduction.
-Organism viz. Planaria reproduce by regeneration in which a fragment of body forms whole organism.
-Fungi,filamentousalgae,protonema of moss reproduce by fragmentation also.
-In unicellular organisms growth & reproduction are synonymous.
1. Certain organisms do not reproduce viz. mule ,worker bees, infertile human couple.
-Hence reproduction cannot be considered as defining property of living beings.
-Several chemical reactions occur in living organisms.-Some of these reactions are anabolic others are catabolic.
-All the reactions together are called metabolic reactions & process is called metabolism.
-It has no exception.
-living organisms consist of cells & their products.
Consciousness: Ability to sense environment & respond to environmental factors
-Living beings sense& respond to environmental factors viz. Light,water,temperature,other organisms, pollutants etc.
Living organisms can be considered as self replicating, evolving & self-regulating interactive systems capable of responding to external stimuli.
Diversity in the living world:
-Described number of species range 1.7-1.8 million.
-Local names of organisms may not be applied at global level.
-Scientific names are given to organisms after identification, acceptable at global level.
-Nomenclature is done as per criteria given in ICBN (International code for botanical nomenclature)& ICZN (International code for zoological nomenclature)
-Binomial nomenclature was given by CAROLUS LINNAEUS.
1.First word is Generic name & second word is Specific epithet in scientific name of organism.
-Names are in Latin or Latinised word.
-Names, if hand written are separately underlined & if printed, are italicised.
-First word starts with capital letter & second word with small letter. Example: Mangifera indica (Mango)
-Name of author in last as abbreviation.
-For ease of study organisms are classified into groups or categories known as taxa.
1.eg. Taxon may be Dogs, Mammals, wheat, Rice etc.
-Process of classification into different taxa is called taxonomy.
-Identification, classification, nomenclature are basic to taxonomy.
-Systematics studies evolutionary relationship between organisms.
-Each rank or category of classification is termed as taxonomic category.
-Arrangement of categories in sequence is termed as Taxonomic Hierarchy.
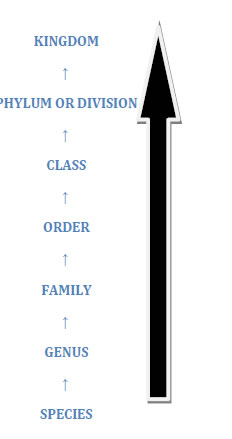
Species: Group of organisms with fundamental similarities. eg. Mangiferaindica
In this species is indica.
Genus: Group of realated specieswith common characters.
eg. Panthera is a genus which includes lion(Pantheraleo),leopard(Pantherapardus) & Tiger (Pantheratigris).
Family: Group of realated genera .
eg. Genus Solanum,Petunia&Datura belong to one family Solanaceae.
Order : Group of related families.
eg. FamaliesConvolvulaceae,Solanaceae belong to one order- Polymoniales.
Class : Group of related orders.
eg. Order Primata&Carnivora belong to one class Mammalia.
Phylum: Group of related classes.
eg. Class Mammalia, Pisces,Amphibia,Reptilia belong to one phylum -Chordata.
Kingdom: Group of all related Phyla.
eg. Kingdom Animalia-includes all animals.
Common |
Biological |
Genus |
Family |
Man |
Homo |
Homo |
Hominidae |
Housefly |
Musca |
Musca |
Muscidae |
Mango |
Mangifera |
Mangifera |
Anacardiaceae |
Wheat |
Triticuma |
Triticum |
Poaceae |
Order |
Class |
Phylum/Division |
Primata |
Mammalia |
Chordata |
Diptera |
Insecta |
Arthropoda |
Sapinda |
Dicotyledonae |
Angiospermae |
Poales |
Monocotyledonae |
Angiospermae |
-Articles helpful in correct identification & classification of organisms are called taxonomical aids.
1.Store house of collected plant specimens that are dried, pressed & preserved on sheets.
-Sheets are arranged according to universally accepted classification system.
-used as ready reference in scientific studies.
Collection of various living plant species in form of gardenfor identification purpose
-Used for identification of plants.
-Example: Royal Botanical Garden at Kew, England, Indian Botanical Garden Howrah, National Botanical Research Institute Lucknow etc.
-Collection of preserved plant &animal specimens.
-Specimens may be preserved in preservative solutions viz.Formalin (40%).
-Specimens may also be preserved as dry specimenseg. Insects and stuffed large animals.
-Skeleton of animals may be also as museum specimen.
-Used as actual material for study and identification.
Place where wild animals are kept in protected environment under human care . eg. Alipur zoo, Kolkata, West Bengal
National Zoological Park of New Delhi
1. Used as aid to learn about food habits and behaviour, Life cycle.
Taxonomical aid based on contrasting characters called as couplet
1. Couplet has two opposite statements, each called lead.
2. Separate keys for separate taxonomic categories needed.
3. Used to classify organism.
Actual account of habitat & distribution of plant species in an area.
•Have description of species in an area.
• Used for getting information foridentification of names.
Monograph :
1. Has information of any one taxon.
2. Used for classification purpose.
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.