
Senior Secondary stage of school education is a stage of transition from general education to discipline-based focus on curriculum. The present updated syllabus keeps in view the rigour and depth of disciplinary approach as well as the comprehension level of learners. Due care has also been taken that the syllabus is comparable to the international standards. Salient features of the syllabus include:Emphasis on basic conceptual understanding of the content.Emphasis on use of SI units, symbols, nomenclature of physical quantities and formulations as per international standards.Providing logical sequencing of units of the subject matter and proper placement of concepts with their linkage for better learning.
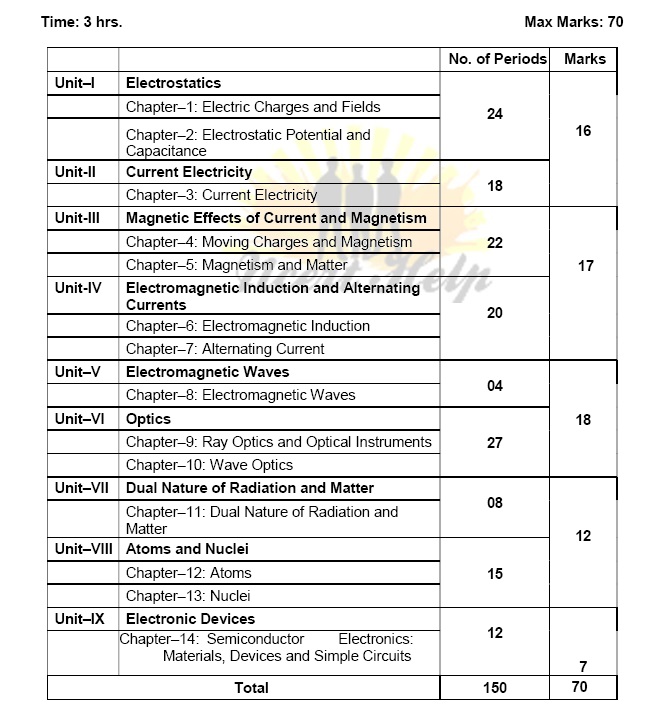
Electric Charges; Conservation of charge, Coulombs law-force between two point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in uniform electric fleld. Electric flux, statement of Gausss theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside).
Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarisation, capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor.
Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohms law, electrical resistance, V-I characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, Carbon resistors, colour code for carbon resistors; series and parallel combinations of resistors; temperature dependence of resistance. Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel, Kirchhoffs laws and simple applications, Wheatstone bridge, metre bridge. Potentiometer - principle and its applications to measure potential difference and for comparing EMF of two cells; measurement of internal resistance of a cell.
Concept of magnetic field, Oersteds experiment. Biot - Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Amperes law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire. Straight and toroidal solenoids (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields, Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; moving coil galvanometer-its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron, magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis, torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field; bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines; earths magnetic field and magnetic elements. Para-, dia- and ferro - magnetic substances, with examples. Electromagnets and factors affecting their strengths, permanent magnets.
Electromagnetic induction; Faradays laws, induced EMF and current; Lenzs Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual induction.
Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only), LCR series circuit, resonance; power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC generator and transformer.
Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves, their characteristics, their Transverse nature (qualitative ideas only). Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and its applications, optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lensmakers formula, magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction of light through a prism. Scattering of light - blue colour of sky and reddish apprearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset. Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers.
Wave optics: Wave front and Huygens principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens principle. Interference, Youngs double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum, resolving power of microscope and astronomical telescope, polarisation, plane polarised light, Brewsters law, uses of plane polarised light and Polaroids.
Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenards observations; Einsteins photoelectric equation-particle nature of light. Experimental study of photoelectric effect Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation, Davisson-Germer experiment (experimental details should be omitted; only conclusion should be explained).
Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherfords model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum.
Composition and size of nucleus, Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma particles/rays and their properties; radioactive decay law, half life and mean life. Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators (qualitative ideas only) Semiconductor diode - I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; Special purpose p-n junction diodes: LED, photodiode, solar cell and Zener diode and their characteristics, zener diode as a voltage regulator.
Class 12 physics syllabus, cbse syllabus class 12 physics, 12 physics syllabus, cbse 12 physics syllabus, cbse syllabus for class 12 physics pdf, weightage of chapters in physics class 12, marks distribution of physics class 12, topics deleted by cbse in physics class 12 2019, cbse class 12 physics syllabus 2020, syllabus physics class 12, ncert class 12 physics syllabus, class 12 physics practical syllabus, class 12 phy syllabus, class 12 physics syllabus 2020
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.