
The present curriculum or syllabus provides the students with updated concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The curriculum also aims at emphasizing the underlying principles that are common to animals, plants and microorganisms as well as highlighting the relationship of Biology with other areas of knowledge. The format of the curriculum allows a simple, clear, sequential flow of concepts. create awareness amongst the learners about diversity in the living organisms and developing respect for other living beings appreciate that the most complex biological phenomena are built on essentially simple processes It is expected that the students would various branches of Biology in the curriculum in a more contextual and systematic manner.
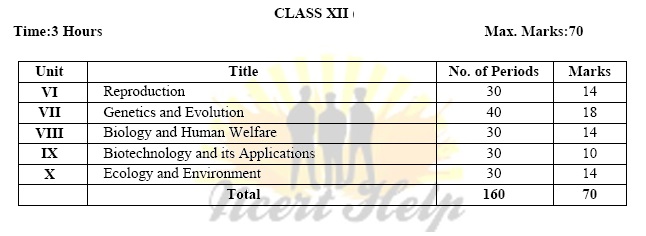
Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; modes of reproduction - asexual and sexual reproduction; asexual reproduction - binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule formation, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants.
Flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination - types, agencies and examples; outbreeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events - development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed dispersal and fruit formation.
Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis - spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea).
Need for reproductive health and prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth control - need and methods, contraception and medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (elementary idea for general awareness). 8
Heredity and variation: Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; Sex determination - in human being, birds and honey bee; linkage and crossing over; sex linked inheritance - haemophilia, colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans -thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Downs syndrome, Turners and Klinefelters syndromes.
Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central Dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation - lac operon; Genome, Human and rice genome projects; DNA fingerprinting.
Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); Darwins contribution, modern synthetic theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution - variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy - Weinbergs principle; adaptive radiation; human evolution.
Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue, chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm) and their control; Basic concepts of immunology - vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence - drug and alcohol abuse.
Animal husbandry, Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein.
Microbes in food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as bio-control agents and bio-fertilizers. Antibiotics; production and judicious use.
Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology). 9
Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, stem cell technology, gene therapy; genetically modified organisms - Bt crops; transgenic animals; biosafety issues, biopiracy and patents.
Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche, population and ecological adaptations; population interactions - mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; population attributes - growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
Ecosystems: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy; nutrient cycles (carbon and phosphorous); ecological succession; ecological services - carbon fixation, pollination, seed dispersal, oxygen release (in brief).
Biodiversity - Concept, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife, sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
Air pollution and its control; water pollution and its control; agrochemicals and their effects; solid waste management; radioactive waste management; greenhouse effect and climate change impact and mitigation; ozone layer depletion; deforestation; case study exemplifying success story addressing environmental issue(s).
Class 12 biology syllabus, class 12 biology syllabus ncert, cbse class 12 biology syllabus, 12th biology syllabus, cbse class 12 biology syllabus pdf, cbse 12 biology syllabus, syllabus biology class 12 up board, biology class 12 up board, class 12 biology practical syllabus, class 12 biology ncert syllabus, syllabus class 12 biology, up board syllabus of class 12th biology pdf, nios syllabus for 12th biology, biology practical class 12 up board, ncert syllabus for class 12 biology practical
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.