
The course in accountancy in commerce stream is introduced at plus two stage of senior second of school education, as the formal commerce education is provided after ten years of schooling. With the fast changing economic scenario, accounting as a source of financial information has carved out a place for itself at the senior secondary stage. The increased role of ICT in all walks of life cannot be overemphasized and is becoming an integral part of business operations. The learners of accounting are introduced to Computerized Accounting System at class XII. Computerized Accounting System is a compulsory component which is to be studied by all students of commerce in class XI; whereas in class XII it is offered as an optional subject to Company Accounts Statements.
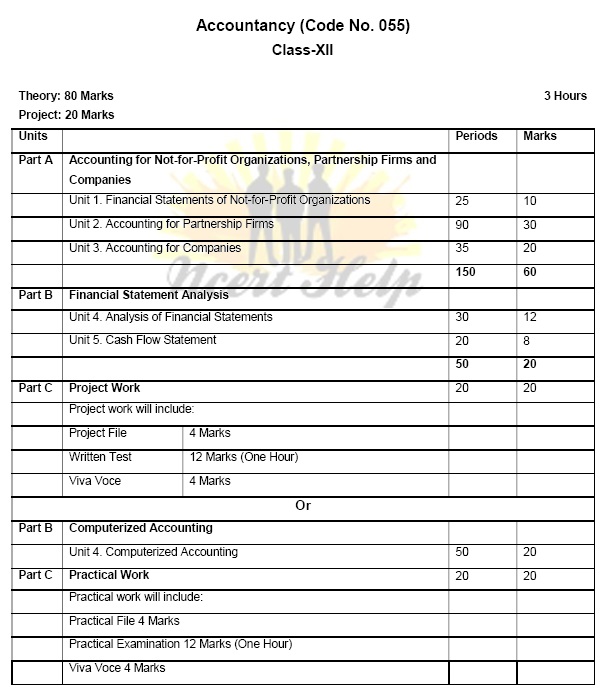
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Not-for-profit organizations: concept. Receipts and Payments Account: features and preparation. Income and Expenditure Account: features, preparation of income and expenditure account and balance sheet from the given receipts and payments account with additional information. Scope: (i) Adjustments in a question should not exceed 3 or 4 in number and restricted to subscriptions, consumption of consumables and sale of assets/ old material. (ii) Entrance/admission fees and general donations are to be treated as revenue receipts. (iii) Trading Account of incidental activities is not to be prepared. After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning of a Not-for-profit organisation and its distinction from a profit making entity. state the meaning of receipts and payments account, and understanding its features. develop the understanding and skill of preparing receipts and payments account. state the meaning of income and expenditure account and understand its features. develop the understanding and skill of preparing income and expenditure account and balance sheet of a not-for-profit organisation with the help of given receipts and payments account and additional information.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Partnership: features, Partnership Deed. Provisions of the Indian Partnership Act 1932 in the absence of partnership deed. Fixed v/s fluctuating capital accounts. Preparation of Profit and Loss Appropriation account- division of profit among partners, guarantee of profits. Past adjustments (relating to interest on capital, interest on drawing, salary and profit sharing ratio). Goodwill: nature, factors affecting and methods of valuation - average profit, super profit and capitalization. Note: Interest on partners loan is to be treated as a After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning of partnership, partnership firm and partnership deed. describe the characteristic features of partnership and the contents of partnership deed. discuss the significance of provision of Partnership Act in the absence of partnership deed. differentiate between fixed and fluctuating capital, outline the process and develop the understanding and skill of preparation of Profit and Loss Appropriation Account. develop the understanding and skill of 13 charge against profits. Goodwill to be adjusted through partners capital/ current account or by raising and writing off goodwill (AS 26) Accounting for Partnership firms - Reconstitution and Dissolution. Change in the Profit Sharing Ratio among the existing partners - sacrificing ratio, gaining ratio, accounting for revaluation of assets and reassessment of liabilities and treatment of reserves and accumulated profits. Preparation of revaluation account and balance sheet. Admission of a partner - effect of admission of a partner on change in the profit sharing ratio, treatment of goodwill (as per AS 26), treatment for revaluation of assets and reassessment of liabilities, treatment of reserves and accumulated profits, adjustment of capital accounts and preparation of balance sheet. Retirement and death of a partner: effect of retirement / death of a partner on change in profit sharing ratio, treatment of goodwill (as per AS 26), treatment for revaluation of assets and reassessment of liabilities, adjustment of accumulated profits and reserves, adjustment of capital accounts and preparation of balance sheet. Preparation of loan account of the retiring partner. Calculation of deceased partner’s share of profit till the date of death. Preparation of deceased partner’s capital account and his executor’s account. Dissolution of a partnership firm: meaning of dissolution of partnership and partnership firm, types of dissolution of a firm. Settlement of accounts - preparation of realization preparation profit and loss appropriation account involving guarantee of profits. develop the understanding and skill of making past adjustments. state the meaning, nature and factors affectin goodwill develop the understanding and skill of valuation of goodwill using different methods. state the meaning of sacrificing ratio, gaining ratio and the change in profit sharing ratio among existing partners. develop the understanding of accounting treatment of revaluation assets and reassessment of liabilities and treatment of reserves and accumulated profits by preparing revaluation account and balance sheet. explain the effect of change in profit sharing ratio on admission of a new partner. develop the understanding and skill of treatment of goodwill as per AS-26, treatment of revaluation of assets and re-assessment of liabilities, treatment of reserves and accumulated profits, adjustment of capital accounts and preparation of balance sheet of the new firm. explain the effect of retirement / death of a partner on change in profit sharing ratio. develop the understanding of accounting treatment of goodwill, revaluation of assets and re-assessment of liabilities and adjustment of accumulated profits and reserves on retirement / death of a partner and capital adjustment. develop the skill of calculation of deceased partners share till the time of his death and prepare deceased partners executors account. discuss the preparation of the capital 14 account, and other related accounts: capital accounts of partners and cash/bank a/c (excluding piecemeal distribution, sale to a company and insolvency of partner(s)). Note: (i) The realized value of each asset must be given at the time of dissolution. (ii) In case, the realization expenses are borne by a partner, clear indication should be given regarding the payment thereof. accounts of the remaining partners and the balance sheet of the firm after retirement / death of a partner. understand the situations under which a partnership firm can be dissolved. develop the understanding of preparation of realisation account and other related accounts.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Accounting for Share Capital Share and share capital: nature and types. Accounting for share capital: issue and allotment of equity and preferences shares. Public subscription of shares - over subscription and under subscription of shares; issue at par and at premium, calls in advance and arrears (excluding interest), issue of shares for consideration other than cash. Concept of Private Placement and Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP). Accounting treatment of forfeiture and reissue of shares. Disclosure of share capital in the Balance Sheet of a company. Accounting for Debentures Debentures: Issue of debentures at par, at a premium and at a discount. Issue of debentures for consideration other than cash; Issue of debentures with terms of redemption; debentures as collateral securityconcept, interest on debentures. Writing off discount / loss on issue of debentures. After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning of share and share capital and differentiate between equity shares and preference shares and different types of share capital. understand the meaning of private placement of shares and Employee Stock Option Plan. explain the accounting treatment of share capital transactions regarding issue of shares. develop the understanding of accounting treatment of forfeiture and re-issue of forfeited shares. describe the presentation of share capital in the balance sheet of the company as per schedule III part I of the Companies Act 2013. explain the accounting treatment of different categories of transactions related to issue of debentures. develop the understanding and skill of writing of discount / loss on issue of debentures. understand the concept of collateral security and its presentation in balance sheet. develop the skill of calculating interest on 15 Note: Discount or loss on issue of debentures to be written off in the year debentures are allotted from Security Premium Reserve (if it exists) and then from Statement of Profit and Loss as Financial Cost (AS 16). Redemption of debentures-Methods: Lump sum, draw of lots. Creation of Debenture Redemption Reserve. Note: Related sections of the Companies Act, 2013 will apply. debentures and its accounting treatment. state the meaning of redemption of debentures. develop the understanding of accounting treatment of transactions related to redemption of debentures by lump sum, draw of lots and Creation of Debenture Redemption Reserve.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Financial statements of a Company: Statement of Profit and Loss and Balance Sheet in prescribed form with major headings and sub headings (as per Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013) Note: Exceptional items, extraordinary items and profit (loss) from discontinued operations are excluded. Financial Statement Analysis: Objectives, importance and limitations. Tools for Financial Statement Analysis: Comparative statements, common size statements, cash flow analysis, ratio analysis. Accounting Ratios: Meaning, Objectives, classification and computation. Liquidity Ratios: Current ratio and Quick ratio. Solvency Ratios: Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Asset to Debt Ratio, Proprietary Ratio and Interest Coverage Ratio. Activity Ratios: Inventory Turnover Ratio, Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio, Trade After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: develop the understanding of major headings and sub-headings (as per Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013) of balance sheet as per the prescribed norms / formats. state the meaning, objectives and limitations of financial statement analysis. discuss the meaning of different tools of financial statements analysis. develop the understanding and skill of preparation of comparative and common size financial statements. state the meaning, objectives and significance of different types of ratios. develop the understanding of computation of current ratio and quick ratio. develop the skill of computation of debt equity ratio, total asset to debt ratio, proprietary ratio and interest coverage ratio. develop the skill of computation of inventory turnover ratio, trade receivables and trade payables ratio and working capital turnover 16 Payables Turnover Ratio and Working Capital Turnover Ratio. Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit Ratio, Operating Ratio, Operating Profit Ratio, Net Profit Ratio and Return on Investment. ratio. develop the skill of computation of gross profit ratio, operating ratio, operating profit ratio, net profit ratio and return on investment. Note: Net Profit Ratio is to be calculated on the basis of profit before and after tax.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Meaning, objectives and preparation (as per AS 3 (Revised) (Indirect Method only) Note: (i) Adjustments relating to depreciation and amortization, profit or loss on sale of assets including investments, dividend (both final and interim) and tax. (ii) Bank overdraft and cash credit to be treated as short term borrowings. (iii) Current Investments to be taken as Marketable securities unless otherwise specified. After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning and objectives of cash flow statement. develop the understanding of preparation of Cash Flow Statement using indirect method as per AS 3 with given adjustments. Note: Previous years’ Proposed Dividend to be given effect, as prescribed in AS-4, Events occurring after the Balance Sheet date. Current years’ Proposed Dividend will be accounted for in the next year after it is declared by the shareholders. 17
Note: Kindly refer to the Guidelines published by the CBSE. The comprehensive project may contain simple GST calculations.
OR
Overview of Computerised Accounting System Introduction: Application in Accounting. Features of Computerised Accounting System. Structure of CAS. Software Packages: Generic; Specific; Tailored. Accounting Application of Electronic Spreadsheet. Concept of electronic spreadsheet. Features offered by electronic spreadsheet. Application in generating accounting information - bank reconciliation statement; asset accounting; loan repayment of loan schedule, ratio analysis Data representation- graphs, charts and diagrams. Using Computerized Accounting System. Steps in installation of CAS, codification and Hierarchy of account heads, creation of accounts. Data: Entry, validation and verification. Adjusting entries, preparation of balance sheet, profit and loss account with closing entries and opening entries. Need and security features of the system. Database Management System (DBMS) Concept and Features of DBMS. DBMS in Business Application. Generating Accounting Information - Payroll.
Class 12 accountancy syllabus, class 12 accounts syllabus, accounts syllabus class 12, cbse syllabus for class 12 accountancy, 12th accounts syllabus, 12th cbse accounts syllabus, nios syllabus for 12th accountancy, cbse class 12th 2019 accountancy syllabus, 12th accountancy new syllabus, icse syllabus for class 12 accountancy, cbse accountancy syllabus, class 12th accounts syllabus, accountancy syllabus class 12, account syllabus class 12, class 12 cbse accountancy syllabus
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.