
Its syllabus content provide students a firm foundation in basic accounting concepts and methodology and also acquaint them with the changes taking place in the preparation and presentation of financial statements in accordance to the applicable accounting standards and the Companies Act 2013. The course in accounting put emphasis on developing basic understanding about accounting as an information system. The emphasis in Class XI is placed on basic concepts and process of accounting leading to the preparation of accounts for a sole proprietorship firm. The students are also familiarized with basic calculations of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in recording the business transactions. The accounting treatment of GST is confined to the syllabus of class XI.
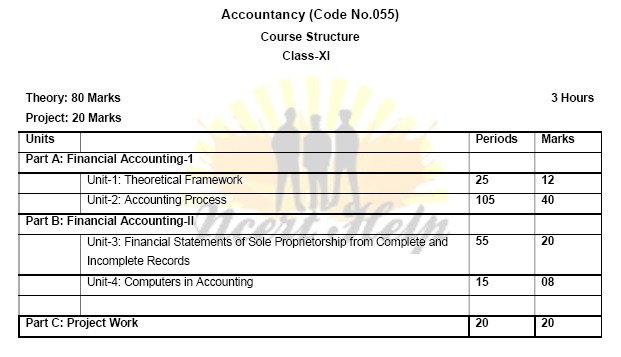
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Introduction to Accounting Accounting- concept, objectives, advantages and limitations, types of accounting information; users of accounting information and their needs. Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information. Role of Accounting in Business. Basic Accounting Terms- Business Transaction, Capital, Drawings. Liabilities (Non Current and Current). Assets (Non Current, Current); Fixed assets (Tangible and Intangible), Expenditure (Capital and Revenue), Expense, Income, Profit, Gain, Loss, Purchase, Sales, Goods, Stock, Debtor, Creditor, Voucher, Discount (Trade discount and Cash Discount) After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: describe the meaning, significance, objectives, advantages and limitations of accounting in the modem economic environment with varied types of business and non-business economic entities. identify / recognise the individual(s) and entities that use accounting information for serving their needs of decision making. explain the various terms used in accounting and differentiate between different related terms like current and non-current, capital and revenue. give examples of terms like business transaction, liabilities, assets, expenditure and purchases. 4 Theory Base of Accounting Fundamental accounting assumptions: GAAP: Concept Business Entity, Money Measurement, Going Concern, Accounting Period, Cost Concept, Dual Aspect, Revenue Recognition, Matching, Full Disclosure, Consistency, Conservatism, Materiality and Objectivity System of Accounting. Basis of Accounting: cash basis and accrual basis Accounting Standards: Applicability in IndAS Goods and Services Tax (GST): Characteristics and Objective. explain that sales/purchases include both cash and credit sales/purchases relating to the accounting year. differentiate among income, profits and gains. state the meaning of fundamental accounting assumptions and their relevance in accounting. describe the meaning of accounting assumptions and the situation in which an assumption is applied during the accounting process. explain the meaning and objectives of accounting standards. appreciate that various accounting standards developed nationally and globally are in practice for bringing parity in the accounting treatment of different items. acknowledge the fact that recording of accounting transactions follows double entry system. explain the bases of recording accounting transaction and to appreciate that accrual basis is a better basis for depicting the correct financial position of an enterprise. Understand the need of IFRS Explain the meaning, objective and characteristic of GST.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Recording of Business Transactions Voucher and Transactions: Source documents and Vouchers, Preparation of Vouchers, Accounting Equation Approach: Meaning and Analysis, Rules of Debit and Credit. Recording of Transactions: Books of Original After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: explain the concept of accounting equation and appreciate that every transaction affects either both the sides of the equation or a positive effect on one item and a negative effect on another item on the same side of 5 Entry- Journal Special Purpose books: Cash Book: Simple, cash book with bank column and petty cashbook Purchases book Sales book Purchases return book Sales return book Note: Including trade discount, freight and cartage expenses for simple GST calculation. Ledger: Format, Posting from journal and subsidiary books, Balancing of accounts Bank Reconciliation Statement: Need and preparation, Bank Reconciliation Statement with Adjusted Cash Book Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves Depreciation: Concept, Features, Causes, factors Other similar terms: Depletion and Amortisation Methods of Depreciation: i. Straight Line Method (SLM) ii. Written Down Value Method (WDV) Note: Excluding change of method Difference between SLM and WDV; Advantages of SLM and WDV Accounting treatment of depreciation i. Charging to asset account ii. Creating provision for depreciation/accumulated depreciation account iii. Treatment for disposal of asset Provisions and Reserves: Difference Types of Reserves: i. Revenue reserve ii. Capital reserve iii. General reserve iv. Specific reserve accounting equation. explain the effect of a transaction (increase or decrease) on the assets, liabilities, capital, revenue and expenses. appreciate that on the basis of source documents, accounting vouchers are prepared for recording transaction in the books of accounts. develop the understanding of recording of transactions in journal and the skill of calculating GST. explain the purpose of maintaining a Cash Book and develop the skill of preparing the format of different types of cash books and the method of recording cash transactions in Cash book. describe the method of recording transactions other than cash transactions as per their nature in different subsidiary books . appreciate that at times bank balance as indicated by cash book is different from the bank balance as shown by the pass book / bank statement and to reconcile both the balances, bank reconciliation statement is prepared. develop understanding of preparing bank reconciliation statement. appreciate that for ascertaining the position of individual accounts, transactions are posted from subsidiary books and journal proper into the concerned accounts in the ledger and develop the skill of ledger posting. explain the necessity of providing depreciation and develop the skill of using different methods for computing depreciation. understand the accounting treatment of providing depreciation directly to the concerned asset account or by creating provision for depreciation account. 6 v. Secret Reserve Difference between capital and revenue reserve Accounting for Bills of Exchange Bill of exchange and Promissory Note: Definition, Specimen, Features, Parties. Difference between Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note Terms in Bill of Exchange: i. Term of Bill ii. Accommodation bill (concept) iii. Days of Grace iv. Date of maturity v. Discounting of bill vi. Endorsement of bill vii. Bill after due date viii. Negotiation ix. Bill sent for collection x. Dishonour of bill xi. Retirement of bill xii. Renewal of bill Accounting Treatment Note: excluding accounting treatment for accommodation bill Trial balance and Rectification of Errors Trial balance: objectives and preparation (Scope: Trial balance with balance method only) Errors: types-errors of omission, commission, principles, and compensating; their effect on Trial Balance. Detection and rectification of errors; preparation of suspense account. appreciate the method of asset disposal through the concerned asset account or by preparing asset disposal account. appreciate the need for creating reserves and also making provisions for events which may belong to the current year but may happen in next year. appreciate the difference between reserve and reserve fund. acquire the knowledge of using bills of exchange and promissory notes for financing business transactions; understand the meaning and distinctive features of these instruments and develop the skills of their preparation. state the meaning of different terms used in bills of exchange and their implication in accounting. explain the method of recording of bill transactions. state the need and objectives of preparing trial balance and develop the skill of preparing trial balance. appreciate that errors may be committed during the process of accounting. understand the meaning of different types of errors and their effect on trial balance. develop the skill of identification and location of errors and their rectification and preparation of suspense account. 7
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Financial Statements Meaning, objectives and importance; Revenue and Capital Receipts; Revenue and Capital Expenditure; Deferred Revenue expenditure. Trading and Profit and Loss Account: Gross Profit, Operating profit and Net profit. Preparation. Balance Sheet: need, grouping and marshalling of assets and liabilities. Preparation. Adjustments in preparation of financial statements with respect to closing stock, outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, accrued income, income received in advance, depreciation, bad debts, provision for doubtful debts, provision for discount on debtors, Abnormal loss, Goods taken for personal use/staff welfare, interest on capital and managers commission. Preparation of Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet of a sole proprietorship with adjustments. Incomplete Records Features, reasons and limitations. Ascertainment of Profit/Loss by Statement of Affairs method. Difference between accounts from incomplete records and Statement of Affairs. Preparation of Trading , Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet. After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning of financial statements the purpose of preparing financial statements. state the meaning of gross profit, operating profit and net profit and develop the skill of preparing trading and profit and loss account. explain the need for preparing balance sheet. understand the technique of grouping and marshalling of assets and liabilities. appreciate that there may be certain items other than those shown in trial balance which may need adjustments while preparing financial statements. develop the understanding and skill to do adjustments for items and their presentation in financial statements like depreciation, closing stock, provisions, abnormal loss etc. develop the skill of preparation of trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet. state the meaning of incomplete records and their uses and limitations. develop the understanding and skill of computation of profit / loss using the statement of affairs method.
Units/Topics Learning Outcomes Introduction to computer and accounting information system {AIS}: Introduction to computers (elements, capabilities, limitations of computer system) Introduction to operating software, utility software and application software. After going through this Unit, the students will be able to: state the meaning of a computer, describe its components, capabilities and limitations. state the meaning of accounting information system. 8 Introduction to accounting information system (AIS) as a part of Management Information System. Automation of accounting process: meaning Stages in automation: (a) Accounting process in a computerised environment; comparison between manual accounting process and computerised accounting process, (b) Sourcing of accounting software; kinds of software: readymade software; customised software and tailor-made software; generic considerations before sourcing accounting software (c) creation of account groups and hierarchy (d) generation of reports - trial balance, profit and loss account and balance sheet Scope: (i) The scope of the Unit is to understand accounting as an information system for the generation of accounting information and preparation of accounting reports. (ii) It is presumed that the working knowledge of any appropriate accounting software will be given to the students to help them learn basic accounting operations on computers. appreciate the need for use of computers in accounting for preparing accounting reports. develop the understanding of comparing the manual and computerized accounting process and appreciate the advantages and limitations of automation. understand the different kinds of accounting software.
1. Collection of source documents, preparation of vouchers, recording of transactions with the help of vouchers. 2. Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement with the given cash book and the pass book with twenty to twenty-five transactions. 3. Comprehensive project of any sole proprietorship business. This may state with journal entries and their ledgering, preparation of Trial balance. Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. Expenses, incomes and profit (loss), assets and liabilities are to be depicted using pie chart / bar diagram.
Accountancy class 11 syllabus, cbse class 11 accountancy syllabus, class 11 account syllabus, accounts syllabus class 11, 11th accounts syllabus, syllabus of accounts class 11, accountancy syllabus class 11, cbse accounts syllabus 11th class, syllabus of accountancy class 11, 11th accountancy syllabus, class 11 cbse accountancy syllabus, 11th account syllabus, 11th cbse accounts syllabus, syllabus of class 11 accountancy, accounts class 11 syllabus, isc class 11 accounts syllabus
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.