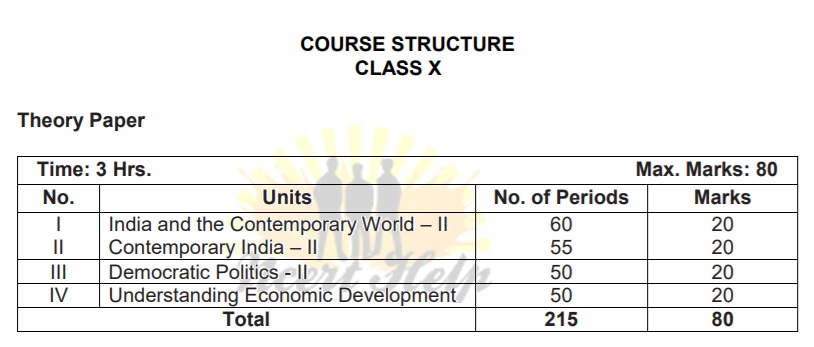
Unit 1: India and the Contemporary World – II 60 Periods
|
Themes | Learning Objectives |
Section 1: Events and Processes - 1. The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
- The French Revolution and the Idea of the Nation
- The Making of Nationalism in Europe
- The Age of Revolutions: 1830-1848
- The Making of Germany and Italy
- Visualizing the Nation
- Nationalism and Imperialism
- 2. Nationalism in India
- The First World War, Khilafat and Non - Cooperation
- Differing Strands within the Movement
- Towards Civil Disobedience
- The Sense of Collective Belonging
| - Enable the learners to identify and comprehend the forms in which nationalism developed along with the formation of nation states in Europe in the post-1830 period.
- Establish the relationship and bring out the difference between European nationalism and anti-colonial nationalisms.
- Understand the way the idea of nationalism emerged and led to the formation of nation states in Europe and elsewhere.
- Recognize the characteristics of Indian nationalism through a case study of Non-Cooperation and Civil Disobedience Movement.
- Analyze the nature of the diverse social movements of the time.
- Familiarize with the writings and ideals of different political groups and individuals.
|
Section 2: Livelihoods, Economies and Societies: Any one theme of the following:
3. The Making of a Global World - The Pre-modern world
- The Nineteenth Century (1815-1914)
- The Inter war Economy
- Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-War Era
4. The Age of Industrialization - Before the Industrial Revolution
- Hand Labour and Steam Power
- Industrialization in the colonies
- Factories Come Up
- The Peculiarities of Industrial Growth
- Market for Goods
Section 3: Everyday Life, Culture and Politics
5. Print Culture and the Modern World - The First Printed Books
- Print Comes to Europe
- The Print Revolution and its Impact
- The Reading Mania
- The Nineteenth Century
- India and the World of Print
- Religious Reform and Public Debates
- New Forms of Publication
- Print and Censorship
| - Appreciate the ideas promoting Pan Indian belongingness.
- Show that globalization has a long history and point to the shifts within the process.
- Analyze the implication of globalization for local economies.
- Discuss how globalization is experienced differently by different social groups.
- Familiarize with the Pro- to-Industrial phase and Early – factory system.
- Familiarize with the process of industrialization and its impact on labour class.
- Enable them to understand industrialization in the colonies with reference to Textile industries.
- Identify the link between print culture and the circulation of ideas.
- Familiarize with pictures, cartoons, extracts from propaganda literature and newspaper debates on important events and issues in the past.
- Understand that forms of writing have a specific history, and that they reflect historical changes within society and shape the forces of change.
|
Unit 2: Contemporary India – II 55 Periods |
Themes | Learning Objectives |
- 1. Resources and Development
- Types of Resources
- Development of Resources
- Resource Planning in India
- Land Resources
- Land Utilization
- Land Use Pattern in India
- Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
- Soil as a Resource
- Classification of Soils
- Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
2. Forest and Wildlife - Biodiversity or Biological Diversity
- Flora and Fauna in India
- Vanishing Forests
- Asiatic Cheetah: Where did they go?
- The Himalayan Yew in trouble
- Conservation of forest and wildlife in India
- Project Tiger
- Types and distribution of forests and wildlife resources
- Community and Conservation
Note: The chapter ‘Forest and Wildlife’ to be assessed in the Periodic Tests only and will not be evaluated in Board Examination.
3. Water Resources - Water Scarcity and The Need for Water Conservation and Management
- Multi-Purpose River Projects and Integrated Water Resources Management
- Rainwater Harvesting
| - Understand the value of resources and the need for their judicious utilization and conservation.
- Understand the importance of biodiversity with regard to flora and fauna in India.
- Analyse the importance of conservation of forests and wildlife.
- Comprehend the importance of water as a resource as well as develop awareness towards its judicious use and conservation.
|
Note: The theoretical aspect of chapter ‘Water Resources’ to be assessed in the Periodic Tests only and will not be evaluated in Board Examination. However, the map items of this chapter as given in the Map List will be evaluated in Board Examination.
4. Agriculture - Types of farming
- Cropping Pattern
- Major Crops
- Technological and Institutional Reforms
- Impact of Globalization on Agriculture
5. Minerals and Energy Resources - What is a mineral?
- Mode of occurrence of Minerals
- Ferrons and Non-Ferrons Minerals
- Non-Metallic Minerals
- Rock Minerals
- Conservation of Minerals
- Energy Resources
- o Conventional and Non-Conventional
- o Conservation of Energy Resources
6. Manufacturing Industries - Importance of manufacturing
- Contribution of Industry to National Economy
- Industrial Location
- Classification of Industries
| - Explain the importance of agriculture in national economy.
- Identify various types of farming and discuss the various farming methods; describe the spatial distribution of major crops as well as understand the relationship between rainfall regimes and cropping pattern.
- Explain various government policies for institutional as well as technological reforms since independence.
- Identify different types of minerals and energy resources and places of their availability
- Feel the need for their judicious utilization
- Bring out the importance of industries in the national economy as well as understand the regional disparities which resulted due to concentration of industries in some areas.
|
- Spatial distribution
- Industrial pollution and environmental degradation
- Control of Environmental Degradation
7. Life Lines of National Economy - Transport – Roadways, Railways, Pipelines, Waterways, Airways
- Communication
- International Trade
- Tourism as a Trade
| - Discuss the need for a planned industrial development and debate over the role of government towards sustainable development.
- Explain the importance of transport and communication in the ever-shrinking world.
- Understand the role of trade and tourism in the economic development of a country.
|
Unit 3: Democratic Politics – II 50 Periods |
Themes | Learning Objectives |
- 1. Power Sharing
- Case Studies of Belgium and Sri Lanka
- Why power sharing is desirable?
- Forms of Power Sharing
- 2. Federalism
- What is Federalism?
- What make India a Federal Country?
- How is Federalism practiced?
- Decentralization in India
- 3. Democracy and Diversity
- Case Studies of Mexico
- Differences, similarities and divisions
- Politics of social divisions
Note: The chapter ‘Democracy and Diversity’ to be assessed in the Periodic Tests only and will not be evaluated in Board Examination. - 4. Gender, Religion and Caste
- Gender and Politics
- Religion, Communalism and Politics
- Caste and Politics
| - Familiarize with the centrality of power sharing in a democracy.
- Understand the working of spatial and social power sharing mechanisms.
- Analyse federal provisions and institutions.
- Explain decentralization in rural and urban areas.
- Analyse the relationship between social cleavages and political competition with reference to Indian situation.
- Identify and analyse the challenges posed by communalism to Indian democracy.
|
- 5. Popular Struggles and Movements
- Popular Struggles in Nepal and Bolivia
- Mobilization and Organization
- Pressure Groups and Movements
Note: The chapter ‘Popular Struggles and Movements’ to be assessed in the Periodic Tests only and will not be evaluated in Board Examination. - 6. Political Parties
- Why do we need Political Parties?
- How many Parties should we have?
- National Political Parties
- State Parties
- Challenges to Political Parties
- How can Parties be reformed?
- 7. Outcomes of Democracy
- How do we assess democracy’s outcomes?
- Accountable, responsive and legitimate government
- Economic growth and development
- Reduction of inequality and poverty
- Accommodation of social diversity
- Dignity and freedom of the citizens
- 8. Challenges to Democracy
- Thinking about challenges
- Thinking about Political Reforms
- Redefining democracy
| - Recognise the enabling and disabling effects of caste and ethnicity in politics.
- Develop a gender perspective on politics.
- Understand the vital role of people’s struggle in the expansion of democracy.
- Analyse party systems in democracies.
- Introduction to major political parties, challenges faced by them and reforms in the country.
- Evaluate the functioning of democracies in comparison to alternative forms of governments.
- Understand the causes for continuation of democracy in India.
- Distinguish between sources of strengths and weaknesses of Indian democracy.
- Reflect on the different kinds of measures possible to deepen democracy.
- Promote an active and participatory citizenship.
|
Note: The chapter ‘Challenges to Democracy’ to be assessed in the Periodic Tests only and will not be evaluated in Board Examination. |
Unit 4: Understanding Economic Development 50 Periods |
Themes | Objectives |
- 1. Development
- What Development Promises - Different people different goals
- Income and other goals
- National Development
- How to compare different countries or states?
- Income and other criteria
- Public Facilities
- Sustainability of development
- 2. Sectors of the Indian Economy
- Sectors of Economic Activities
- Comparing the three sectors
- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors in India
- Division of sectors as organized and unorganized
- Sectors in terms of ownership: Public and Private Sectors
- 3. Money and Credit
- Money as a medium of exchange
- Modern forms of money
- Loan activities of Banks
- Two different credit situations
- Terms of credit
- Formal sector credit in India
- Self Help Groups for the Poor
- 4. Globalization and the Indian Economy
- Production across countries
- Interlinking production across countries
| - Familiarize with concepts of macroeconomics.
- Understand the rationale for overall human development in our country, which includes the rise of income, improvements in health and education rather than income.
- Understand the importance of quality of life and sustainable development.
- Identify major employment generating sectors.
- Reason out the government investment in different sectors of economy.
- Understand money as an economic concept.
- Understand the role of financial institutions from the point of view of day-to- day life.
- Explain the working of the Global Economic phenomenon.
|
- Foreign Trade and integration of markets
- What is globalization?
- Factors that have enabled Globalisation
- World Trade Organisation
- Impact of Globalization on India
- The Struggle for a fair Globalisation
- 5. Consumer Rights
Note: Chapter 5 ‘Consumer Rights’ to be done as Project Work. | - Gets familiarized with the rights and duties as a consumer; and legal measures available to protect from being exploited in markets.
|
Cbse chapterwise marks distribution class 10 social science, 10th social science book, class 10 sst syllabus, social science class 10 syllabus, sst syllabus class 10, cbse class 10 sst syllabus, social science class 10th cbse, cbse syllabus for class 10 social science pdf, syllabus of sst class 10 cbse 2019, class 10 sst syllabus 2019, up board class 10 social science syllabus, sst syllabus of class 10, social science textbook class 10 state syllabus, up board class 10 social science book