
Ncert Solutions for class 9 subject Science Chapter 6 Tissuein pdf Best Free NCERT Solutions for class 1 to 12 in pdf NCERT Solutions, cbse board, Science, ncert Solutions for Class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, Tissue, Class 9, ncert solutions chapter 6 Tissue, class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, Science ncert solutions class 9, Ncert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue
In text questions of page no 69
Q No 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans: In multicellular organisms, several cells are grouped to form tissues. These tissues perform particular function at a definite place in the body. For example, nerve cells from the nervous tissue which helps in transmission of messages. This is known as ision of labour in multicellular organisms. Because of this ision of labour, multicellular organisms are able to perform all functions perfectly.
In text questions of page no 74
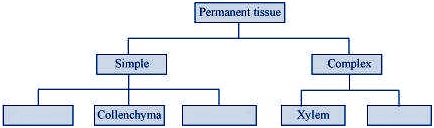
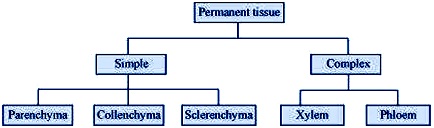
Q No 1: Name types of simple tissues.
Ans: Simple permanent tissues are of three types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma. Parenchyma is two types
Q No 2: Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. They ide very fast which are responsible for the growth of roots tip and shoots tip.
Q No 3: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
Q No 4: What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of plants. It is made up of four components:
In text questions of page no 78
Q No 1: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Ans: The muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Q No 2: What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm. It has two important extensions known as the dendrites and axon.
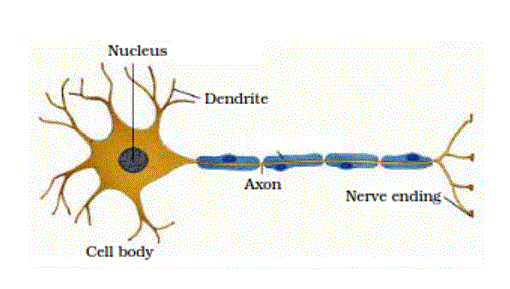
A Nerve Cell
Q No 3: Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans: Three features of cardiac muscles are:
Q No 4: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Functions of areolar tissue are:-
Q No 1: Define the term “tissue”.
Ans: A group of cells that are similar in structure and functions grouped together to form a tissue.
Q No 2: How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans: There are four different types of cells that make up the xylem tissue. They are:-
Q No 3: How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Ans:
| Simple tissue | Complex tissue |
Simple tissues consist of onlyone type of cells |
These tissues are made up of morethan one type of cells. |
The cells of simpletissue perform similar function. |
The cells of complextissue may perform different functions. |
Example of simpletissues are collenchymas, parenchyma. |
Examples of complextissues are xylem and phloem. |
Q No 4: Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, on the basis of their cell wall.
Ans:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma |
Sclerenchyma |
Cell wall is thin |
Cell wall is thick |
Cell wall is very thickalso hard and rigid |
Q No 5: What are the functions of the stomata?
Ans: Functions of the stomata:
Q No 6: Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans:
The three types of muscle fibres are:- Striated muscles, smooth muscles and cardiac muscles.
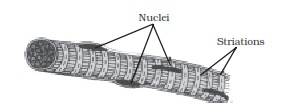
Striated muscle fibres
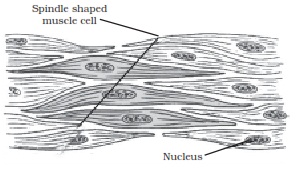
Smooth muscle fibres
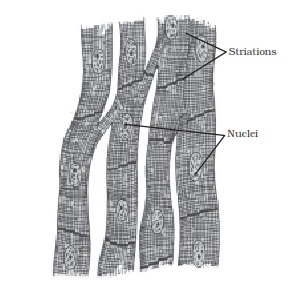
Cardiac muscle fibres
Q No 7: What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: The specific function of the cardiac muscle is to control the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Q No 8: Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans:
| Striated muscle | Unstriated muscle |
Cardiac muscle |
They are cylindrical inshape and multi nucleate. |
They spindle shaped anduninucleate. |
They are cylindricalbranched and uninucleate. |
They are present inbody parts such as hands and legs. |
They are present in thewall of food canal, stomach, mouth, iris etc. |
They are present in theheart. |
Q No 9: Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Ans:

Structure of a neuron
Q No 10: Name the following:
Ans:
Q No 11: Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Ans:
Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Bark of tree: cork (secondary meristem)
Bone: Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithilium
Vascular bundle: Complex permanent tissue (Xylem and Phloem)
Q No 12: Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans: The parenchyma tissue is present in leaves, fruits, and flowers of a plant.
Q No 13: What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Ans: Epidermis is present on the outer surface of the whole plant body. The cells of the epidermal tissue form a continuous layer without any intercellular space. It performs the following important functions:-
Q No 14: How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans: Cells of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a chemical called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water thus they provide strong mechanical strength to plants.
Q No 15: Complete the table:
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.