
Ncert Solutions for class 9 subject Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Lifein pdf Best Free NCERT Solutions for class 1 to 12 in pdf NCERT Solutions, cbse board, Science, ncert Solutions for Class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, The Fundamental Unit Of Life, Class 9, ncert solutions chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life, class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, Science ncert solutions class 9, Ncert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Define a cell. Who discovered cell?
Cells are the fundamental structural units of living organisms and the basic units of life. Robert Hooke discovered the cell in the year 1665 as a thin section of cork under the self made microscope.
Who discovered first living cell?
Leeuwenhoek discovered the free living cells in pond water for the first time.
In the year 1674, with the help of improved microscope.
How does the cell of a onion peel look like?
The cell of onion peel looks like as following
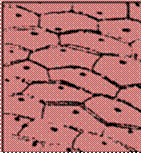
Who discovered nucleus in the cell?
Robert Brown discovered the nucleus in the cell in the year of in 1831.
Who coined the term ‘protoplasm’ for the fluid substance of the cell?
J. E. Purkinje in the year 1839 coined the term ‘protoplasm’ for the fluid substance of the cell.
Who gave the cell theory? Who expanded it further?
The cell theory which states that all the plants and animals are composed of cells and that the cell is the basic unit of life was presented by two biologists, Schleiden (1838) and Schwann (1839).
Who gave the cell theory that the cell comes from the pre existing cell?
The theory that the every cell comes from pre existing cell was given by Virchow in the year of 1855.
What are unicellular organisms? Give some examples.
When all the vital functions which are necessary for life are performed by a single cell then such cell is called unicellular organism. Some examples of unicellular organisms are Amoeba, Paramecium etc.
What are cell organelles? Give some examples?
Various components presents inside a cell are known as cell organelles. For example plasma membrane, nucleus cytoplasm all are cell organelles.
What is plasma membrane?
This is the outermost covering of the cell that separates the contents of the cell from its external environment. The plasma membrane allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. The cell membrane, therefore, is called a
selectively permeable membrane.
Define osmosis.
The movement of water from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi permeable membrane is known as osmosis.
What is diffusion?
The movement of gases (like carbon dioxide and oxygen) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi permeable membrane is known as diffusion. Thus, diffusion plays an important role in gaseous exchange between the cells as well as the cell and its external environment.
What is a hypotonic solution?
If the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell, meaning that the outside solution is very dilute, the cell will gain water by osmosis. Such a solution is known as a hypotonic solution.
Water molecules are free to pass across the cell membrane in both directions, but more water will come into the cell than will leave. The net (overall) result is that water enters the cell. The cell is likely to swell up.
What is a isotonic solution?
If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Such a solution is known as an isotonic solution. Water crosses the cell membrane in both directions, but the amount going in is the same as the amount going out, so there is no overall movement of water. The cell will stay the same size.
What is a hypertonic solution?
If the medium has a lower concentration of water than the cell, meaning that it is a very concentrated solution, the cell will lose water by osmosis. Such a solution is known as a hypertonic solution. Again, water crosses the cell membrane in both directions, but this time more water leaves the cell than enters it. Therefore the cell will shrink.
What is a cell wall?
Plant cells, in addition to the plasma membrane, have another rigid outer covering called the cell wall. The cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane. The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose. Cellulose is a complex substance and provides structural strength to plants.
What is nucleus?
Nucleus is the largest cell organelle. It is spherical in shape or oval in initial stage (also known as nucleoid). It is usually located in the centre of the cell. Important parts of nucleus are nuclear membrane and chromatin material.
What is cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is the fluid content inside the plasma membrane. It also contains many specialised cell organelles. Each of these organelles performs a specific function for the cell.
What is Endoplasmic Reticulum? Write its types.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membrane-bound tubes and sheets. It looks like long tubules or round. There are two types of ER– rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). RER looks rough under a microscope because it has particles called
ribosomes attached to its surface. The ribosomes, which are present in all active cells, are the sites of protein manufacture. The manufactured proteins are then sent to various places in the cell depending on need, using the ER. The SER helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function.
What is Golgi apparatus? Who discovered it?
The Golgi apparatus, first described by Camillo Golgi, consists of a system of
membrane-bound vesicles arranged approximately parallel to each other in stacks called cisterns. The functions of Golgi apparatus include the storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles. In some cases, complex sugars may be made from simple sugars in the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus is also involved in the formation of lysosomes.
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are a kind of waste disposal system of the cell. Lysosomes help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles. Lysosomes are able to do this because they contain powerful digestive enzymes capable of breaking down all organic material. During the disturbance in cellular metabolism, for example, when the cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst and the enzymes digest their own cell. Therefore, lysosomes are also known as the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell.
What are mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules. ATP is known as the energy currency of the cell. The body uses energy stored in ATP for making new chemical compounds and for mechanical work. Mitochondria are strange organelles in the sense that they have their own DNA and ribosomes. Therefore, mitochondria are able to make some of their own proteins.
What are Plastids?
Plastids are present only in plant cells. There are two types of plastids – chromoplasts (coloured plastids) and leucoplasts (white or colourless plastids). Plastids containing the pigment chlorophyll are known as chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are important for photosynthesis in plants.
The internal organisation of the plastids consists of numerous membrane layers embedded in a material called the stroma. Plastids are similar to mitochondria in external structure. Like the mitochondria, plastids also have their own DNA and ribosomes.
What are Vacuoles?
Vacuoles are storage sacs for solid or liquid contents. Vacuoles are small sized in animal cells while in plant cells they are very large. The central vacuole of some plant cells may occupy 50-90% of the cell volume. In plant cells vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell.
Many substances of importance in the life of the plant cell are stored in vacuoles. These include amino acids, sugars, various organic acids and some proteins.
Draw a labelled diagram of a animal cell.
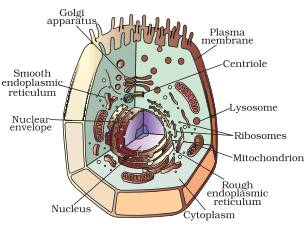
Draw a labelled diagram of a plant cell.
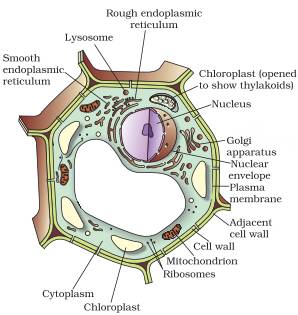
In text questions page number 59
1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered the cells. He saw that the cork resembled the structure of a honeycomb consisting of many little compartments. Cork is a substance which comes from the bark of a tree. This was in the year 1665 when Hooke made this chance observation through a self-designed microscope. Robert Hooke called these boxes cells. In this way he discovered the cells.
2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: Cells are called the structural and functional unit of life because all the living organisms are made up of cells and also all the functions taking place inside the body of organisms are performed by cells.
In text questions page number 61
1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer: Gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen move in and out of a cell by diffusion from the region of high concentration to low concentration.
2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: The membrane is called selectively permeable membrane because it allows selective materials like gases water and wastes not all to move in and out of a cell.
In text questions page number 63
1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.

| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Size : generally small ( 1-10 µm) Where 1 µm = 10-6m | 1.Size: generally large ( 5-100 µm) |
| 2. Nuclearregion: It is not well defined and known as nucleoid. | 2. Nuclearregion: well defined and surrounded bya nuclear membrane |
| 3.Chromosome: single | 3. More than onechromosome |
| 4.Membrane-bound cell organelles absent | 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles arepresent. |
In text questions page number 65
1. Can you name the two organelles? we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer: The cell organelles plastids and mitochondria have their own genetic material.
2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: The damaged cell will not able to perform vital functions like respiration nutrition, removing wastes and making proteins.
3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer: Lysosomes are called suicide bags because in case of disturbance of their cellular metabolism they digest their own cell by releasing own enzymes.
4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis inside a cell. They are either free or attached to Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(RER).
1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. They are larger in size. | 1. They aresmaller in size. |
| 2. Cell wall is present. | 2. Cell wall isabsent. |
| 3. Lysosomes are absent or very few in number | 3. Lysosomesare larger in number. |
| 4. Plastids are present. | 4. Plastids areabsent. |
| 5. Subunits of Golgi bodies known as dictyosomes are present. | 5. ProminentGolgi bodies are present. |
| 6. Vacuoles are larger in size. | 6. Vacuoles aresmaller in size. |
2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Size : generally small ( 1-10 µm) Where 1 µm = 10-6m | 1.Size: generally large ( 5-100 µm) |
| 2. Nuclear region: It is not well defined and known as nucleoid. | 2. Nuclearregion: well defined and surrounded bya nuclear membrane |
| 3.Chromosome: single | 3. More than onechromosome |
| 4.Membrane-bound cell organelles absent | 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles arepresent. |
3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: If the plasma membrane ruptures or breakdown then the cell will not be able to exchange material from its surrounding by diffusion or osmosis. Thereafter the protoplasmic material will be disappeared and the cell will die.
4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: Golgi apparatus has the function of storage modification and packaging of the products. If there is no Golgi apparatus then the packaging and transporting of materials synthesized by cell will not happen.
5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules.
6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer: Lipids are synthesized in Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the proteins are synthesized in rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer: Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle forming a food-vacuole as shown in figure. Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones which then diffuse into the cytoplasm. The remaining undigested material is moved to the surface of the cell and thrown out.
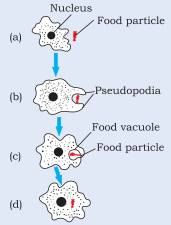
8. What is osmosis?
Answer: Osmosis is the process in which water molecules moves from the region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi permeable membrane.
9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoops each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out
Portions of A and D.
Answer:
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.