
Ncert Solutions for class 9 subject Science Chapter 2 IS Matter Around Us Purein pdf Best Free NCERT Solutions for class 1 to 12 in pdf NCERT Solutions, cbse board, Science, ncert Solutions for Class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, IS Matter Around Us Pure, Class 9, ncert solutions chapter 2 IS Matter Around Us Pure, class 9 Science, class 9 Science ncert solutions, Science ncert solutions class 9, Ncert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 2 IS Matter Around Us Pure
What is a pure substance? Name the types of pure substances.
Answer: Any substance is said to be pure if and only if it is made up of single type of particles means all the particles of that substance should be of same chemical nature. For example water, sugar, salt, Sodium, Tin etc.
There are two types of pure substances that are Elements and Compounds.
Examples of elements are: Iron, Silver, Gold, Mercury etc.
Examples of compounds are: Water, Carbon dioxide, methane, vinegar etc.
What is a solution? Write its properties.
Answer: A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A solution has a solvent and a solute as its components.The component of the solution that dissolves the other component in it (usually the component present in larger amount) is called the solvent.The component of the solution that is dissolved in the solvent (usually present in lesser quantity) is called the solute.
Properties of a solution
• A solution is a homogeneous mixture.
• The particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm (10-9 metre) in diameter. So, they cannot be seen by naked eyes.
• Because of very small particle size, they do not scatter a beam of light passing through the solution. So, the path of light is not visible in a solution.
• The solute particles cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration. The solute particles do not settle down when left undisturbed,
that is, a solution is stable.
Concentration of Solution: Concentration of a solution is the amount of solute present in the given amount of solution. The concentration of a solution can be determined by the following ways:
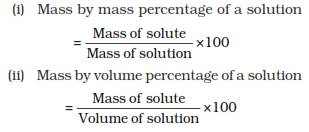
What is a suspension? Write its properties.
Answer: Suspension: A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solids are dispersed in liquids. The solute particles in suspension do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the medium. For example Paints, Muddy water chalk water mixtures etc.
Properties of a Suspension
• Suspension is a heterogeneous Mixture.
• The particles of a suspension can be seen by the naked eye.
• The particles of a suspension scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
• The solute particles settle down when a suspension is left undisturbed, that is, a suspension is unstable. They can be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration.
What is a colloid? Write its properties.
Answer: Colloid: A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture whose particles are not as small as solution but they are so small that cannot be seen by naked eye. When a beam of light is passed through a colloid then the path of the light becomes visible. For example milk, smoke etc.
Properties of a colloid
• A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture.
• The size of particles of a colloid is too small to be inidually seen by naked eyes.
• Colloids are big enough to scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
• They do not settle down when left undisturbed, that is, a colloid is quite stable.
• They cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration. But, a special technique of separation known as centrifugation can be used to separate the colloidal particles.
What is a Tyndall effect?
Answer: This scattering of a beam of light by the particles of a colloid is called the Tyndall effect. When we apply torch light on a galss of milk then the path of the light becomes visible but it is not so in case of water because in milk light is scattered by its very fine particles. See the following diagram: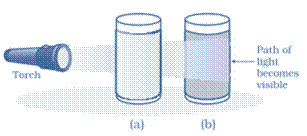
Tyndall effect can be observed when sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest. In the forest, mist contains tiny droplets of water, which act as particles of colloid dispersed in air. If is shown in the diagram below:

What are the various methods for separating the components of a mixture?
Answer:
| S No | Name of Method | Example |
| 1 | Evaporation | To get coloured component (dye) fromink. |
| 2 | Centrifugation | To separate cream from milk. |
| 3 | Use of Separating funnel | To separate two immiscible liquids likekerosene and water. |
| 4 | Sublimation | To separate a mixture of ammonium chlorideand salt. |
| 5 | Chromatography | Separation of dyes in blue/black ink. |
| 6 | Distillation | To separate two miscible liquids like alcoholand water. |
| 7 | Crystallisation | To obtain pure solid from impure samples likesalt from sea water. |
| 8 | Winnowing | To separate food grains from the husk. |
| 9 | Filtrations | To separate sand from the water. |
| 10 | Sedimentation | To remove the heavier impurities present inliquids. |
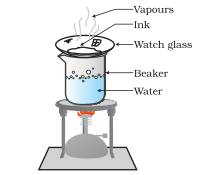
How can we obtain the coloured component (dye) from a ink?
Answer: Put a watch glass on the mouth of the beaker as shown in the given figure. Put few drops of ink on the watch glass. Now start heating the beaker. We do not want to heat the ink directly. You will see that evaporation is taking place from the watch glass. Continue heating as the evaporation goes on and stop heating when you do not see any further change on the watch glass.
Now we will observe that the water get evaporated from the watch glass and residue is left in the watch glass. This residue is the coloured component (Dye). In this way evaporation can used to obtain volatile component from its solution.
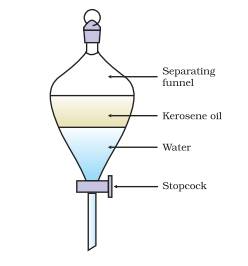
Explain the use of separating funnel.
Answer: A separating funnel can be used to separate the components of the mixture of immiscible liquids. How this can be done? To understand this let us perform a following activity.
Let us try to separate kerosene oil from water using a separating funnel.
Pour the mixture of kerosene oil and water in a separating funnel.
Let it stand undisturbed for sometime so that separate layers of oil and water are formed. Open the stopcock of the separating funnel and pour out the lower layer of water carefully. Now close the stopcock of the separating funnel as the oil reaches the stop-cock.
Applications
• To separate mixture of oil and water.
• In the extraction of iron from its ore, the lighter slag is removed from the top by this method to leave the molten iron at the bottom in the furnace.
Explain sublimation.
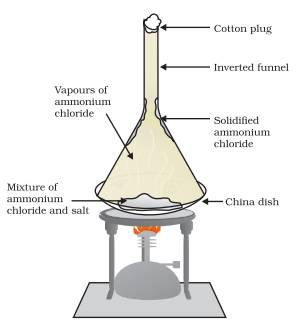
Answer: Sublimation is the property of substance in which they are converted directly from solid to gas or vice versa. Such substances are known as sublime. Some examples of solids which sublime are ammonium chloride, camphor, naphthalene and anthracene. Let us perform an activity to separate a mixture of ammonium chloride and salt.
Take a mixture of ammonium chloride and salt in a china dish cover it inverted conical transparent funnel. At the other end of the funnel put a cotton plug so that vapour could not come out. Now place china dish on a burner. As the ammonium chloride is sublime after heating it will directly converted into vapour and this vapour will again condense at the upper colder part of funnel to form solid ammonium chloride. In this way the mixture ammonium chloride and salt can be separated by the sublimation method.
Explain Centrifugation.
Answer: Sometimes the solid particles in a liquid are very small and pass through a filter paper. For such particles the filtration technique cannot be used for separation. Such mixtures are separated by centrifugation. The principle is that the denser particles are forced to the bottom and the lighter particles stay at the top when spun rapidly.
Explain Chromatography.
Answer: Chromatography is the technique used for separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent.
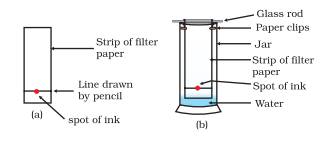
To understand how this technique can be used let us perform an activity.
Take a thin strip of filter paper. Draw a line on it using a pencil, approximately 3 cm above the lower edge as shown in figure(a). Put a small drop of ink (water soluble, that is, from a sketch pen or fountain pen) at the centre of the line. Let it dry. Lower the filter paper into a jar/glass/ beaker/test tube containing water so that the drop of ink on the paper is just above the water level, as shown in Fig(b) and leave it undisturbed.
Watch carefully, as the water rises up on the filter paper. Now observe that the coloured component that is more soluble in water, rises faster and in this way colours get separated.
Applications of Chromatography
To separate
• colours in a dye
• pigments from natural colours
• drugs from blood.
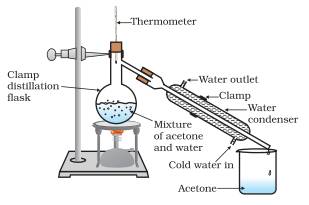
Explain the method of simple distillation.
Answer: This method is used to separate the mixture of two miscible liquids where difference between their boiling points is at least 25 ºC.
Acetone and water are miscible liquids also the difference between their boiling point is more than 25 ºC so they can be separated by the method of simple distillation. Follow the steps given below
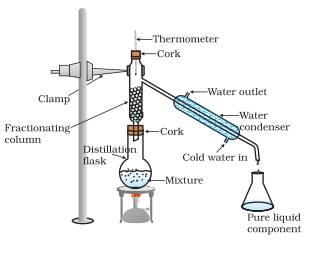
Explain the method of fractional distillation.
Answer: This method is used to separate the mixture of two miscible liquids where difference between their boiling points is less than 25 ºC. Also to separate a mixture of two or more miscible liquids for which the difference in boiling points is less than 25 K, fractional distillation process is used, for example, for the separation of different gases from air, different factions from petroleum products etc. The apparatus is similar to that for simple distillation, except that a fractionating column is fitted in between the distillation flask and the condenser. A simple fractionating column is a tube packed with glass beads. The beads provide surface for the vapours to cool and condense repeatedly, as shown in following figure.
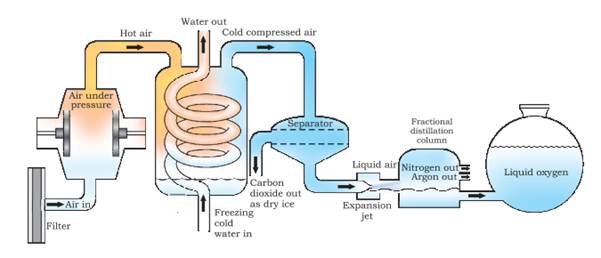
How can we obtain different gases from air?
Answer: Air is a homogeneous mixture and can be separated into its components by fractional distillation. The flow diagram given under shows the steps of the process.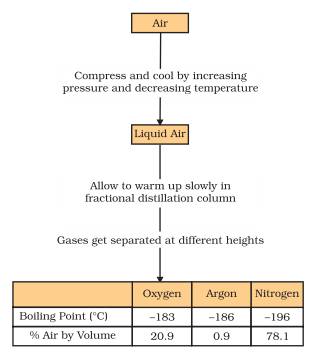
If we want oxygen gas from air, we have to separate out all the other gases present in the air. The air is compressed by increasing the pressure and is then cooled by decreasing the temperature to get liquid air. This liquid air is allowed to warm-up slowly in a fractional distillation column, where gases get separated at different heights depending upon their boiling points.
Explain Crystallisation.
Answer: Crystallisationis a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution. The crystallisation method is used topurify solids.
For example, the salt we get from sea water can have many impurities in it. To remove these impurities, the process of crystallisation is used.
Applications of crystallisation
• Purification of salt that we get from sea water.
• Separation of crystals of alum (phitkari) from impure samples.
What is a physical change? Give example.
Answer: A change which occurs without a change in the composition and chemical nature of the substance is called a physical change. It means that there is a change only in the physical properties of the substance. Properties like colour, hardness, rigidity, fluidity, density, melting point and boiling point are known as physical properties. Melting of ice or boiling of water is a physical change because ice, water and water vapours are chemically the same substance that is H2O.
What is a chemical change? Give example.
Answer: A change in which a substance reacts with another substance to undergo a change in chemical composition. For example burning of a candle in which wax burns and converted into carbon dioxide and water.
Draw the diagram of water purification system in water works.
Answer: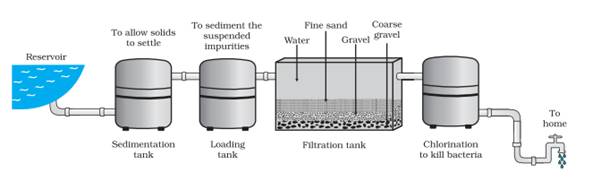
Differentiate between mixtures and compounds.
Answer: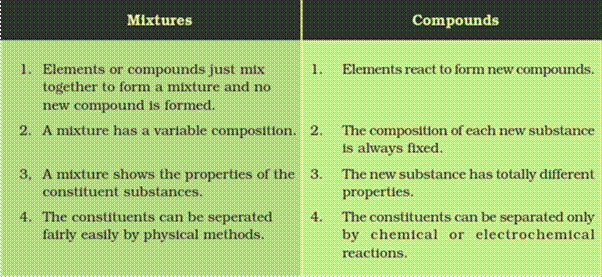
Draw the classification table of matter.
Answer: 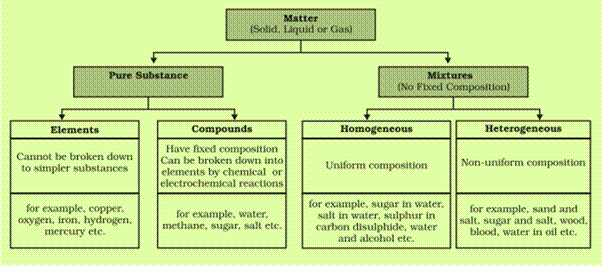
In text questions page number 15
1. What is meant by a pure substance?
Answer: A pure substance consists of single type of particles that is all the constituent particles of a pure substance have same chemical nature. For example all elements and compounds (Na, NaCl etc) are substance.
2. List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Answer:
| Homogeneous Mixtures | HeterogeneousMixtures |
| 1. Homogeneous mixtures have uniform composition. | 1.Heterogeneous mixtures have non uniform composition |
| 2. It has no visible boundaries of separation between itsconstituents. | 2. It hasvisible boundaries of separation between its constituents. |
| 3. Some examples of homogeneous mixtures are: salt in water, sugarin water. | 3. Someexamples of heterogeneous mixtures are: water and sand, oil and water. |
In text questions page number 18
1. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
Answer:
| Homogeneous Mixtures | HeterogeneousMixtures |
| 1. Homogeneous mixtures have uniform composition. | 1.Heterogeneous mixtures have non uniform composition |
| 2. It has no visible boundaries of separation between itsconstituents. | 2. It hasvisible boundaries of separation between its constituents. |
| 3. Some examples of homogeneous mixtures are: salt in water, sugarin water. | 3. Someexamples of heterogeneous mixtures are: water and sand, oil and water. |
2. How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
Answer:
| Sol(Colloidal solution) | Solution | Suspension |
| 1.They are heterogeneous in nature | 1.They arehomogeneous in nature | 1.They areheterogeneous in nature |
| 2. They scatter a beam of light and hence show Tyndall effect. | 2. They do notscatter a beam of light and hence do not show Tyndall effect. | 2. They do notscatter a beam of light and hence do not show Tyndall effect. |
| 3. They are quite stable | 3. They arevery stable | 3. They areunstable |
| 4. Examples of sol are: milk, blood smoke etc. | 4. Examples ofsolution are: salt in water, sugar in water. | 4. Examples ofsuspension are: sand in water, dusty air |
3. To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Answer:
Mass of solute (sodium chloride) =36g
Mass of solvent (water) =100g
Mass of solution = Mass of Solute + Mass of solvent
= 36g +100g = 136g

In text questions page number 24
1. How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25ºC), which are miscible with each other?
Answer: kerosene and petrol are miscible liquids also the difference between their boiling point is more than 25 ºC so they can be separated by the method of distillation. Follow the steps given below
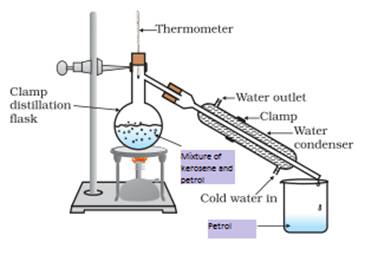
2. Name the technique to separate
(i) butter from curd,
(ii) salt from sea-water,
(iii) camphor from salt.
Answer:
3. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Answer:
Crystallisationis a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution. The crystallisation method is used to purify solids. For example, the salt we get from sea water can have many impurities in it. To remove these impurities, the process of crystallisation is used.
In text questions page number 24
Answer:
(i) Cutting of trees is a physical change.2. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Answer:
Pure substances: drinking water, gold, sugar, salt etc.
Mixtures: Air, Cold drinks, soil, brass etc.
Question 1. Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water.
(b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride.
(c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car.
(d) Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
(e) Butter from curd.
(f) Oil from water.
(g) Tea leaves from tea.
(h) Iron pins from sand.
(i) Wheat grains from husk.
(j) Fine mud particles suspended in water.
Answer:
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water ![]() Evaporation.
Evaporation.
(b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride ![]() Sublimation.
Sublimation.
(c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car ![]() Filtration
Filtration
(d) Different pigments from an extract of flower ![]() Chromatography.
Chromatography.
(e) Butter from curd ![]() Centrifugation.
Centrifugation.
(f) Oil from water ![]() Using separating funnel
Using separating funnel
(g) Tea leaves from tea ![]() Filtration
Filtration
(h) Iron pins from sand ![]() Magnetic Separation
Magnetic Separation
(i) Wheat grains from husk ![]() Winnowing
Winnowing
(j) Fine mud particles suspended in water ![]() Centrifugation.
Centrifugation.
Question 2. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Answer:
(i) Tea can be prepared by following steps:Take 100ml of water as solvent and boil it few minutes.
(ii) Now add one tea spoon sugar, one tea spoon tea leaves and 50ml of milk. Here sugar, tea leaves and milk are solute.
(iii) Now boil it again for few minutes so that sugar will dissolves in solution as sugar is soluble in water
(iv) Now filter the solution. Collect the filtrate in cup. The insoluble tea leaves will be left behind as residue.
Question 3. Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
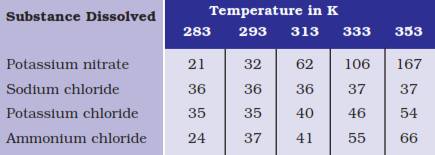
(a) What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 50 grams of water at 313 K?
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. Which salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
Answer:
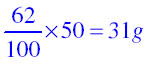 of potassium nitrate.
of potassium nitrate.Question 4. Explain the following giving examples.
(a) saturated solution
(b) pure substance
(c) colloid
(d) suspension
Answer:
Question 5. Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture.
Soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea.
Answer:
Homogeneous mixtures: Soda water, air, vinegar and filtered tea.
Heterogeneous mixtures: wood and soil.
Question 6. How would you confirm that a colourless liquid given to you is pure water?
Answer: Take a sample of colourless liquid and put on stove if it starts boiling exactly at 100 ºC then it is pure water. Any other colourless liquid such as vinegar always have different boiling point. Also observe carefully that after some time whole liquid will convert into vapour without leaving any residue.
Question 7. Which of the following materials fall in the category of a “pure substance”?
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air.
Answer: Out of the above substances only Ice, Iron, Hydrochloric acid, Calcium oxide and Mercury are pure substance.
Question 8. Identify the solutions among the following mixtures.
(a) Soil
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water.
Answer: Out of the above mixtures Sea water, Air and Soda water are solution.
Question 9. Which of the following will show “Tyndall effect”?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution.
Answer: Tyndall effect is shown by colloidal solution. Here milk and starch solution are colloids therefore milk and starch solution will show Tyndall effect.
Question 10. Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures.
(a) Sodium
(b) Soil
(c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver
(e) Calcium carbonate
(f) Tin
(g) Silicon
(h) Coal
(i) Air
(j) Soap
(k) Methane
(l) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Answer:
Classification of the given substances in elements compounds and mixtures
Elements: Sodium, Silver, Tin and Silicon.
Compounds: Calcium carbonate, Methane and carbon dioxide.
Mixtures: Soil, Sugar, Coal, Air, Soap and Blood.
Question 11. Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of a candle.
Answer: Examples of chemical changes are
Growth of plant, Rusting of Iron, Cooking of food, Digestion of food, and burning of candle.
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.