
Ncert Solutions for class 11 subject Physics Chapter 3 Motion In A Straight Linein pdf Best Free NCERT Solutions for class 1 to 12 in pdf NCERT Solutions, cbse board, Physics, ncert Solutions for Class 11 Physics, class 11 Physics ncert solutions, Motion In A Straight Line, Class 11, ncert solutions chapter 3 Motion In A Straight Line, class 11 Physics, class 11 Physics ncert solutions, Physics ncert solutions class 11, Ncert Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion In A Straight Line
Rectilinear motion
Motion of objects along a straight line is known as rectilinear motion.
Reference point
The point of intersection of three mutually perpendicular axes, labelled as X, Y, and Z axes is called origin (O) and serves as the reference point.
Frame of reference
The coordinates (x, y. z) of an object along with a clock in a system constitutes a frame of reference.
Path length
Path length is a scalar quantity. Total distance covered by object is known as path length.
Displacement
Displacement is a vector quantity. The difference between final and initial position is known as displacement. The magnitude of displacement cannot more than path length.
Let x1 and x2 be the positions of an object at time t1 and t2.
Then its displacement, Δx = x2– x1
If x2> x1, Δx is positive; and if x2< x1,Δx is negative.
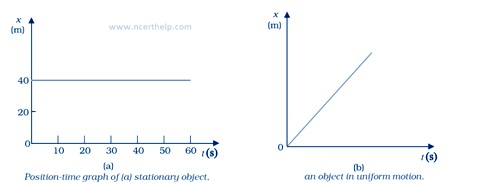
Average velocity
Average velocity is defined as the change in position or displacement (Δx) ided by the time intervals (Δt).it is a vector quantity.
\[\overline v = \frac{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}} = \frac{{\Delta x}}{{\Delta t}}\]
Where x1 and x2 be the positions of an object at time t1 and t2.
The SI unit for velocity is m/s or m s–1
Average speed
Average speed is defined as the total path length travelled by object ided by the total time interval during which the motion has taken place. it is a scalar quantity.
\[{\rm{Average}}\;{\rm{speed = }}\frac{{{\rm{Total}}\;{\rm{path}}\;{\rm{length}}}}{{{\rm{Total}}\;{\rm{time}}\;{\rm{interval}}}}\]
The SI unit for speed is m/s or m s–1
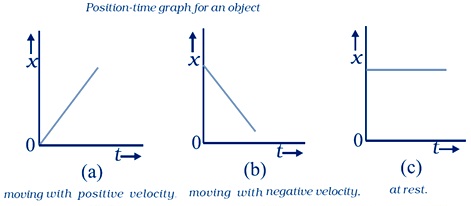
Instantaneous velocity
Velocity of an object at a particular instant is known as instantaneous velocity of that instant. In Instantaneous velocity Δt becomes infinitesimally small.
Instantaneous velocity,${v_{ins}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\Delta t \to 0} {{\Delta x} \over {\Delta t}} = {{dx} \over {dt}}$ .
Instantaneous velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time, at that instant.
For uniform motion, Instantaneous velocity is the same as the average velocity at all instants.
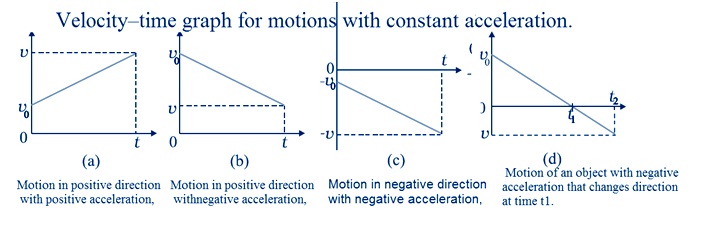
Average acceleration
The average acceleration aavg over a time interval is defined as the change of velocity ided by the time interval
$$\overline a = {{{v_2} - {v_1}} \over {{t_2} - {t_1}}} = {{\Delta v} \over {\Delta t}}$$
Where v1 and v2 be the velocity of an object at time t1 and t2.
It is vector quantity.
Instantaneous acceleration
Acceleration of an object at a particular instant is known as instantaneous acceleration of that instant. In Instantaneous acceleration Δt becomes infinitesimally small.
Instantaneous acceleration,${a_{ins}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\Delta t \to 0} {{\Delta v} \over {\Delta t}} = {{dv} \over {dt}}$ .
Instantaneous acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time, at that instant.

Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.