
Ncert Solutions for class 10 subject Science Chapter 6 Life Processesin pdf Best Free NCERT Solutions for class 1 to 12 in pdf NCERT Solutions, cbse board, Science, ncert Solutions for Class 10 Science, class 10 Science ncert solutions, Life Processes, Class 10, ncert solutions chapter 6 Life Processes, class 10 Science, class 10 Science ncert solutions, Science ncert solutions class 10, Ncert Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Question 1. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition.
(b) respiration.
(c) excretion.
(d) transportation.
Question 2. The xylem in plants are responsible for
(a) transport of water.
(b) transport of food.
(c) transport of amino acids.
(d) transport of oxygen.
Ans.(a)
Question 3. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(a) carbon dioxide and water.
(b) chlorophyll.
(c) sunlight.
(d) all of the above.
Ans.(d)
Question 4. The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(a) cytoplasm.
(b) mitochondria.
(c) chloroplast.
(d) nucleus.
Ans.(b)
Question 5. How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Ans.Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine receives the secretions from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts (from the liver) break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzyme lipase can easily act on them. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. This process takes place in the small intestine.
Question 6. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Ans.Saliva contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar. It also moistens the food for easy swallowing.
Question 7. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by- products?
Ans.Autotrophic nutrition takes place through the process of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll pigment, and sunlight are the necessary conditions required for autotrophic nutrition. Carbohydrates (food) and O2 are the by-products of photosynthesis.
Question 8. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Ans.
Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
It occurs in the presence of O2. | It occurs in the absence of O2. |
It involves the exchange of gases. | Exchange of gases is does not happen. |
It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria. | It occurs only in cytoplasm. |
It always releases CO2and H2O. | End products vary. |
Question 9. How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Ans. Alveoli provide a surface for the exchange of gases. An extensive network of blood vessels is present in the wall of the alveoli. By lifting our ribs and flatten the diaphragm, the chest cavity becomes spacious. Air is sucked into the lungs and alveoli. The oxygen from the breath, diffuses into the blood and CO2 from the blood brought from the body, diffuses out into the air.
Question 10. What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Ans. Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment that transports oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Therefore, deficiency of haemoglobin in blood can affect the oxygen supplying capacity of blood which leads to deficiency of oxygen in the body cells. It can also lead to a disease called anaemia.
Question 11. Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Ans. During a single cycle blood goes twice in the heart which is known as double circulation. It is necessary in human being to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood because this makes their circulatory system is more efficient and helps in maintaining constant body temperature.
Question 12. What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Ans.
Transportof materials in xylem | Transportof materials in phloem |
Xylemtissue helps in the transport of water and minerals. | Phloemtissue helps in the transport of food. |
Wateris transported upwards from roots to aerial parts of plants | Foodis transported in both upward and downward directions. |
Transportin xylem requires physical forces such as transpiration pull. | Transportof food in phloem requires energy in the form of ATP. |
Question 13. Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Ans.
Alveoli | Nephrons |
Structure | Structure |
(i) Alveoli are tiny balloon-like structurespresent inside the lungs. | (i) Nephrons are tubular structures presentinside the kidneys. |
(ii) The walls of the alveoli are one cell thickand it contains an extensive network of blood capillaries. | (ii) Nephrons are made of glomerulus, bowman’scapsule, and a long renal tube. |
Function | Function |
(i) The exchange of O2and CO2takes place between the blood of the capillaries that surround thealveoli and the gases present in the alveoli. | (i) The blood enters the kidneys through therenal artery. The blood is entered here and the nitrogenous waste in the formof urine is collected by collecting duct. |
(ii) Alveoli are the site of gaseous exchange. | (ii) Nephrons are the basic filtration unit. |
In text questions of page 95 ( Life Processes class 10 )
Question 1. Why is the process of simple diffusion sufficient for taking in food, exchange of gases and removal of waste in unicellular organism but not sufficient in multicellular organism?
Ans. The process of simple diffusion is sufficient to carry different activities of life in unicellular organisms as in them, the entire surface of the organism is in contact of the environment. In case of multicellular organisms all the cells are not in direct contact of the environment so simple diffusion will not work.
Question 2. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans.Visible movement such as walking, breathing, or growing is generally used to decide whether something is alive or not. Sometime, a living organism can have movements that are not visible to the naked eye. Therefore, the presence of life processes is a fundamental criteria that can be used to decide whether something is alive or not.
Question 3. What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Ans.An organism uses outside raw materials mostly in the form of food and oxygen. The raw materials required by an organism can be varied depending on the complexity of the organism and its environment.
Question 4. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life
Ans. Life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, etc. are essential for maintaining life.
In text questions of page 101 (Life Processes class 10)
Question 1. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans.
| Autotrophic nutrition | Heterotrophic nutrition |
| <>(i). Food is prepared from CO2, water and sunlight | <>(i). Food is obtained from other organisms. |
| <>(ii). Chlorophyll is required. | <>(ii). Chlorophyll is not required. |
| <>(iii). All green plants and some bacteria have this type of nutrition. | <>(iii).All animals and fungi have this type of nutrition. |
| <>(iv). Food is generally in day time. | <>(iv).Food can be obtained at all time. |
Question 2. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Ans.Light energy from sun, carbon dioxide from air and water from soil.
Question 3. What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Ans.HCl creates the acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin
Question 4. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Ans. Digestive enzymes such as amylase, lipase, pepsin, trypsin, etc. help in the breaking down of complex food particles into simple ones. These simple particles can be easily absorbed by the blood and thus transported to all the cells of the body
Question 5. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Ans. To digest the carbohydrates, fats and proteins, the small intestine receives the secretions of the liver and pancrease. The acidic food coming from the stomach is made alkaline for the action of pancreatic enzymes. The liver secretions have bile juice. The bile salts break the larger fat globules into the smaller one for the effective action of enzymes (emulsification of fats). The walls of small intestine contain glands which secrete intestinal juice. This contains enzymes to convert: Proteins àamino acids Complex Carbohydrates àglucose Fats àfatly acids & glycerol The digested food components are absorbed into the walls of the intestine.
In text questions of page 105 ( Life Processes class 10 )
Question 1. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans.Terrestrial organisms take up oxygen from the atmosphere whereas aquatic animals obtain oxygen from water. Air contains more O2 as compared to water. Since the content of O2 in air is high, the terrestrial animals do not have to breathe faster to get more oxygen. Therefore, unlike aquatic animals, terrestrial animals do not need adaptations for gaseous exchange.
Question 2. Sketch a flow diagram for the various pathways for breakdown of glucose.
Ans.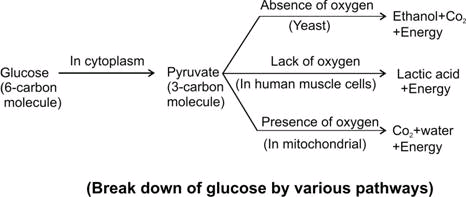
Question 3. How is oxygen and Cardbon Dioxide Transported in human beings?
Ans.Haemoglobin present in RBC is respiratory pigment in Human being which transport Oxygen molecule. When this oxygen is used then blood becomes deoxygenated as it now contains CO2. As CO2 is dissolved in water so it is transported in dissolved form in blood.
Question 4. How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases?
Ans. Lungs contain millions of alveoli which provide a surface for the exchange of gases. An extensive network of blood vessels is present in the wall of the alveoli. By lifting our ribs and flatten the diaphragm, the chest cavity becomes spacious. Air is sucked into the lungs and alveoli. The oxygen from the breath, diffuses into the blood and CO2 from the blood brought from the body, diffuses out into the air.
In text questions of page 110
Question 1. What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Ans.The main components of the transport system in human beings are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. Heart pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body. It receives deoxygenated blood from the various body parts and sends this impure blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Blood helps in the transport of oxygen, nutrients, CO2, and nitrogenous wastes. Blood vessels arteries and veins carry blood in all parts of body.
Question 2. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Ans.It is necessary in mammals and birds to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood because this makes their circulatory system is more efficient and helps in maintaining constant body temperature.
Question 3. What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
Ans.Highly organised plants have two important tissues for their transport system one is Xylem and other is Phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to aerial parts of the plant and Phloem transport food from leaves to other parts of the plants.
Question 4. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans. The vascular tissue Xylem transports water and minerals in plants. Transpiration creates a suction pressure, as a result of which water is forced into the xylem cells of the roots. Then there is a steady movement of water from the root xylem to all the plant parts.
Question 5. How is food transported in plants?
Ans. Phloem transports food materials from the leaves to different parts of the plant. The transportation of food in phloem is achieved by utilizing energy from ATP which helps in creating osmotic pressure that transport food from the area of high concentration to low concentration.
In text questions of page 112 ( Life Processes class 10 )
Question 1. Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Ans.Nephrons are the filtration units of kidney. Each kidney has a large no. of nephrons. The process starts with filteration of urine.

Question 2. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Ans.Plants get rid of:
1. of water by transpiration.
2. waste products may be stored in vacuoles or may be stored in leaves which fall off.
3. resine and gums are stored in xylem.
4. some waste substance may be excreted in the soil.
5. as by products move out of the plants by diffusion through stomata.
Question 3. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Ans.The amount of urine produced depends on the amount of excess water and dissolved wastes present in the body.
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.