
Question 17 What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism. Chapter 1: the Solid State Chemistry Class 12 solutions are developed for assisting understudies with working on their score and increase knowledge of the subjects. What is a semiconductor, Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism is solved by our expert teachers. You can get ncert solutions and notes for class 12 chapter 1 absolutely free. NCERT Solutions for class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1: the Solid State is very essencial for getting good marks in CBSE Board examinations
Question 17 What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism.
AnswerSemiconductors allow to flow a very small quantity of electric current through them at the room temperature. These are the solids with conductivities in the intermediate range from 10–6 to 104 ohm–1m–1.Semiconductors are perfect insulator at absolute zero. Silicon and Germanium are examples of semiconductor.
There are two types of main semiconductors
(i) n–type semiconductor (ii) p–type semiconductor
(i) n–type semiconductor:
there semiconductors have Electron – rich impurities. Silicon and germanium belong to group 14 of the periodic table and each has four valence electrons . Four out of five electrons are used in the formation of four covalent bonds with the four neighbouring silicon atoms. Extra fifth electron is becomes delocalized. These delocalized electrons increase the conductivity of doped silicon or germanium both . Here the increase in conductivity is due to the negatively charged mobile electron. Hence semiconductors doped with electron–rich impurity are called n–type semiconductor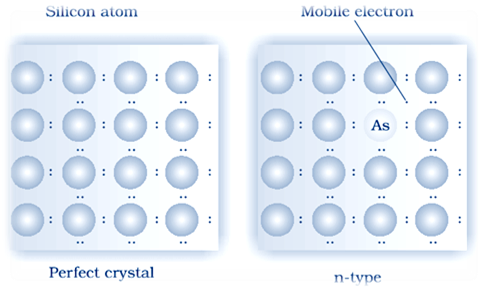
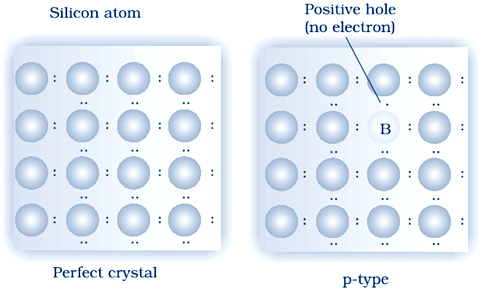
(ii) p–type semiconductor: Si or Ge can also be doped with a group 13 element. The elements of group 13 contains only three valence electrons. Elements of 14th group have has 4 valence electron. The place where the fourth valence electron is missing is called electron hole .An electron from a neighbouring atom can come and fill the electron hole, but in doing so it would leave an electron hole at its original position. If it happens, it would appear as if the electron hole has moved in the direction opposite to that of the electron that filled it. Under the influence of electric field, electrons would move towards the positively charged plate through electronic holes, but it would appear as if electron holes are positively charged and are moving towards negatively charged plate. This type of semi conductors are called p–type semiconductors.
Copyright @ ncerthelp.com A free educational website for CBSE, ICSE and UP board.